Family Gatherings
This ritual is held on or about the day of St. Martin, a Catholic saint who was given many of Odin’s original attributes. There is strong evidence that this day (Nov 12) was originally a festival time devoted to Odin and to Cernunnos, who has many similarities to the Wanderer.
This is a time of festival for several families gathered together, each bringing food and drink for the potluck feast. Prior to the time of the rites, have a day of games and feasting. The ritual should be held out of doors if possible, with the area appropriately decorated for the season with grain, fruits, maize, vegetables, nuts, leaves and flowers. Some of the last remaining Halloween decorations may be used for a final time on this day. place banners of Odin and Freya at the northern edge of the ritual area, or some appropriate other symbols of the female and male in the Divine. Whatever symbols are used, light a candle or torch before each of them.
At the beginning of the rites, the Master of the House summons the celebrants by the blowing of a horn. When all are gathered, he and the Lady of the House light candles and give them to all of the children present; then they lead the children in procession about the perimeter of the ritual area. Upon the return of the slow procession to the starting point, they instruct the small ones to place their lamps at the edge of the ceremonial area, saying:
Place this light
At the edge of our festival
So that the Great Ones
May be with us.
When all are in readiness, the Master of the House raises his hand and says:
Friends, I now bid thee
To join in a celebration
To our patron, the wise Odin,
Known also by his other names
Of Cernunnos and St Martin
The Lady of the House then says:
We call too upon Our Blessed Lady,
The good Freya
Queen of the Harvests, giver of life
And of plenty
Since before time began.
The Master of the House calls to the assembled family members:
Let us all give thanks
For the foods of the harvest, and
For the Challenge of the hunt.
May the wise Allfather bless our homes
And bless our animals, one and all.
So mote it be.
Everyone responds:
So mote it be.
The Lady of the House then calls:
Let us all give thanks
For the fullness of this time,
For the rich promise of the harvest time,
And for the love which binds our families
And our people.
May the Holy Lady bless our homes,
Our families, and all we own.
So mote it be.
Everyone responds
So mote it be.
Both then link hands and call to the assembled family members:
May our Lord and Blessed Lady
Give blessings upon us.
Let us give joy and reveling
Before the Great Ones,
And in so doing, honor them.
This rite is ended.
The Gods be with thee.
Everyone together:
The Gods be with thee.
The children are then asked to blow out the candles that they have set about the area of the ceremony.
From The Rites of Odin
Saint Martin’s Day, also known as the Feast of Saint Martin, Martinstag or Martinmas, as well as Old Halloween and Old Hallowmas Eve, is the feast day of Saint Martin of Tours (Martin le Miséricordieux) and is celebrated on November 11 each year. This is the time when autumn wheat seeding was completed, and the annual slaughter of fattened cattle produced “Martinmas beef”. Historically, hiring fairs were held where farm laborers would seek new posts.
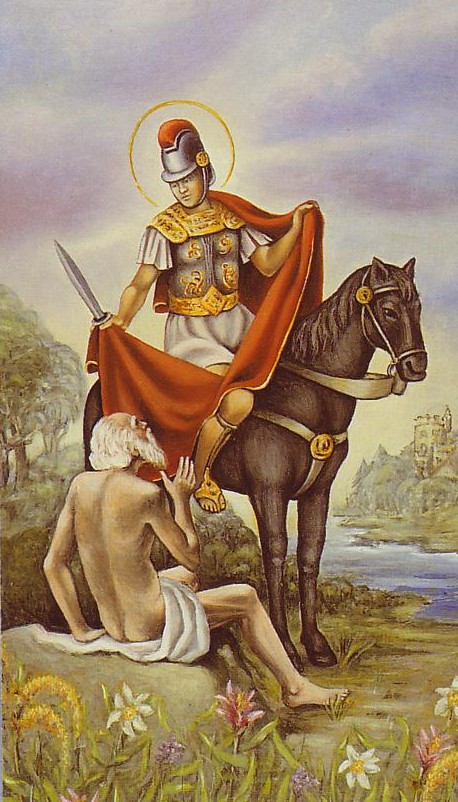
Saint Martin of Tours started out as a Roman soldier then was baptized as an adult and became a monk. It is understood that he was a kind man who led a quiet and simple life. The best known legend of his life is that he once cut his cloak in half to share with a beggar during a snowstorm, to save the beggar from dying from the cold. That night he dreamed that Jesus was wearing the half-cloak. Martin heard Jesus say to the angels, “Here is Martin, the Roman soldier who is now baptized; he has clothed me.”
St. Martin was known as friend of the children and patron of the poor. This holiday originated in France, then spread to the Low Countries, the British Isles, Germany, Scandinavia, and Eastern Europe. It celebrates the end of the agrarian year and the end of the harvest.
Bishop Perpetuus of Tours, who died in 490, ordered fasting three days a week from the day after Saint Martin’s Day (11 November). In the 6th century, local councils required fasting on all days except Saturdays and Sundays from Saint Martin’s Day to Epiphany (the Feast of the Three Wise Men and the star, c.f. Matthew 2: 1-12) on January 6, a period of 56 days, but of 40 days fasting, like the fast of Lent. It was therefore called Quadragesima Sancti Martini (Saint Martin’s Lent). This period of fasting was later shortened and called “Advent” by the Church.
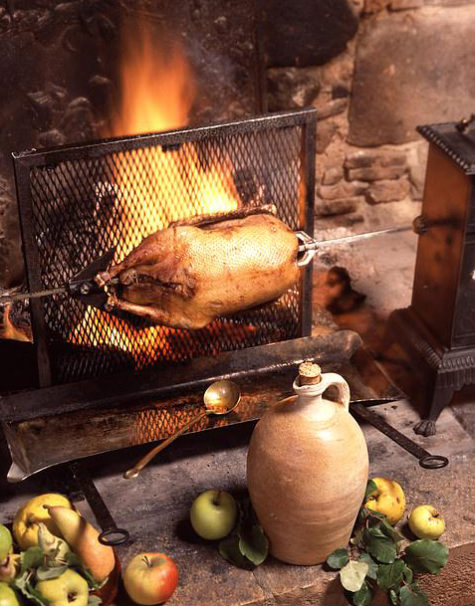
The goose became a symbol of St. Martin of Tours because of a legend that when trying to avoid being ordained bishop he had hidden in a goose pen, where he was betrayed by the cackling of the geese. St. Martin’s feast day falls in November, when geese are ready for killing.
St. Martin’s Day was an important medieval autumn feast, and the custom of eating goose spread to Sweden from France. It was primarily observed by the craftsmen and noblemen of the towns. In the peasant community, not everyone could afford to eat goose, so many ate duck or hen instead.
Martinmas
Martinmas literally means “Mass of Martin”, or the day when Catholics celebrate the Holy Catholic Mass which honors St. Martin in a special way.
Martinmas, as a date on the calendar, has two meanings: in the agricultural calendar it marks the beginning of the natural winter, but in the economic calendar it is seen as the end of autumn. The feast coincides not only with the end of the Octave of All Saints, but with harvest-time, the time when newly produced wine is ready for drinking, and the end of winter preparations, including the butchering of animals.
An old English saying is “His Martinmas will come as it does to every hog,” meaning “he will get his comeuppance” or “everyone must die”. Because of this, St. Martin’s Feast is much like the American Thanksgiving – a celebration of the earth’s bounty. Because it also comes before the penitential season of Advent, it is seen as a mini “carnivale”, with all the feasting and bonfires.
As at Michaelmas on 29 September, goose is eaten in most places. Following these holidays, women traditionally moved their work indoors for the winter, while men would proceed to work in the forests.
In some countries, Martinmas celebrations begin at the eleventh minute of the eleventh hour of this eleventh day of the eleventh month (that is, at 11:11 am on November 11). In others, the festivities commence on St. Martin’s Eve (that is, on November 10). Bonfires are built and children carry lanterns in the streets after dark, singing songs for which they are rewarded with candy.
It is also a day of wine tasting and drinking.
Celebrations around the world:
- Austria
“Martinloben” is celebrated as a collective festival. Events include art exhibitions, wine tastings, and live music. “Martinigansl” (roasted goose) is the traditional dish of the season. In Austria St. Martin’s Day is celebrated the same way as in Germany.The nights before and on the night of Nov. 11, children walk in processions carrying lanterns, which they made in school, and sing Martin songs.
- Belgium
The day is celebrated on the evening of November 11 in a small part of Belgium (mainly in the east of Flanders and around Ypres). Children go through the streets with paper lanterns and candles, and sing songs about St. Martin. Sometimes, a man dressed as St. Martin rides on a horse in front of the procession.
In some areas, there is a traditional goose meal, although in West Flanders there is no specific meal; in other areas it is more a day for children, with toys brought on the night of 10 to 11 November. In the east part of the Belgian province of West Flanders, especially around Ypres, children receive presents from either their friends or family as supposedly coming from St. Martin on November 11. In other areas it is customary that children receive gifts later in the year from either their friends or family as supposedly coming from Saint Nicholas on December 5 or 6 (called Sinterklaas in Belgium and the Netherlands) or Santa Claus on December 25.
In other areas, children go from door to door, singing traditional “Sinntemette” songs, sporting a hollow beetroot with a carved face and a candle inside. Later in the evening there is a bonfire where all of them gather. At the end the beetroots are thrown into the fire, and pancakes are being served.
- Croatia, Slovenia
In Croatia, St. Martin’s Day (Martinje, Martinovanje) marks the day when the must traditionally turns to wine. The must is usually considered impure and sinful, until it is baptized and turned into wine. The baptism is performed by someone who dresses up as a bishop and blesses the wine; this is usually done by the host. Another person is chosen as the godfather of the wine. The foods traditionally eaten on the day are goose and home-made or store bought mlinci.
The biggest event in Slovenia is the St. Martin’s Day celebration in Maribor which marks the symbolic winding up of all the wine growers’ endeavours. There is the ceremonial “christening” of the new wine, and the arrival of the Wine Queen. The square Trg Leona Štuklja is filled with musicians and stalls offering autumn produce and delicacies.
- Slovakia
In Slovakia, the Feast of St. Martin is like a “2nd Birthday” for those named after this saint. Small presents or money are common gifts for this special occasion. Tradition says that if it snows on the feast of St. Martin, November 11, then St. Martin came on a white horse and there will be snow on Christmas day. However, if it doesn’t snow on this day, then St. Martin came on a dark horse and it will not snow on Christmas.
- Czech Republic
A Czech proverb connected with the Feast of St. Martin – Martin přijíždí na bílém koni (trans. “Martin is coming on a white horse”) – signifies that the first half of November in the Czech Republic is the time when it often starts to snow. St. Martin’s Day is the traditional feast day in the run-up to Advent.
Roasted goose is usually found on restaurant menus, and the Czech version of Beaujolais nouveau, Svatomartinské víno, a young wine from the recent harvest, which has recently become more widely available and popular. Wine shops and restaurants around Prague pour the first of the St. Martin’s wines at 11:11 a.m. Many restaurants offer special menus for the day, featuring the traditional roast goose.
- Denmark
In Denmark, Mortensaften, meaning the evening of St. Martin, is celebrated with traditional dinners, while the day itself is rarely recognized. (Morten is the Danish vernacular form of Martin.) The background is the same legend as mentioned above, but nowadays the goose is most often replaced with a duck due to size, taste and/or cost.
- Estonia
In Estonia, Martinmas signifies the merging of Western European customs with local Balto-Finnic pagan traditions. It also contains elements of earlier worship of the dead as well as a certain year-end celebration that predates Christianity. For centuries mardipäev (Martinmas) has been one of the most important and cherished days in the Estonian folk calendar. It remains popular today, especially among young people and the rural population. Martinmas celebrates the end of the agrarian year and the beginning of the winter period.
Among Estonians, Martinmas also marks the end of the period of All Souls, as well as the autumn period in the Estonian popular calendar when the souls of ancestors were worshiped, a period that lasted from November 1 to Martinmas (November 11). On this day children disguise themselves as men and go from door to door, singing songs and telling jokes to receive sweets.
In Southern Estonia, November is called Märtekuu after St. Martin’s Day.
- Germany
A widespread custom in Germany is bonfires on St. Martin’s eve, called “Martinsfeuer.” In recent years, the processions that accompany those fires have been spread over almost a fortnight before Martinmas. At one time, the Rhine River valley would be lined with fires on the eve of Martinmas. In the Rhineland region, Martin’s day is celebrated traditionally with a get-together during which a roasted suckling pig is shared with the neighbors.
The nights before and on the night of Nov. 11, children walk in processions carrying lanterns, which they made in school, and sing Martin songs. Usually, the walk starts at a church and goes to a public square. A man on horseback dressed like St. Martin accompanies the children. When they reach the square, Martin’s bonfire is lit and Martin’s pretzels are distributed.
In some regions of Germany (e.g. Rhineland or Bergisches Land) in a separate procession the children also go from house to house with their lanterns, sing songs and get candy in return.
The origin of the procession of lanterns is unclear. To some, it is a substitute for the St. Martin bonfire, which is still lit in a few cities and villages throughout Europe. It formerly symbolized the light that holiness brings to the darkness, just as St. Martin brought hope to the poor through his good deeds. Even though the tradition of the large, crackling fire is gradually being lost, the procession of lanterns is still practiced.
The tradition of the St. Martin’s goose or “Martinsgans”, which is typically served on the evening of St. Martin’s feast day following the procession of lanterns, most likely evolved from the well-known legend of St. Martin and the geese. “Martinsgans” is usually served in restaurants, roasted, with red cabbage and dumplings.
In some regions of Germany, the traditional sweet of Martinmas is “Martinshörnchen”, a pastry shaped in the form of a croissant, which recalls both the hooves of St. Martin’s horse and, by being the half of a pretzel, the parting of his mantle. In parts of western Germany these pastries are instead shaped like men (Stutenkerl or Weckmänner).
- Great Britain
In the United Kingdom, St. Martin’s Day is known as Martinmas (or sometimes Martlemass). It is one of the term days in Scotland. Many schools celebrate St. Martin’s day. Many schools are also named after St. Martin.
Martlemass beef was from cattle slaughtered at Martinmas and salted or otherwise preserved for the winter. The now largely archaic term “St. Martin’s Summer” referred to the fact that in Britain people often believed there was a brief warm spell common around the time of St. Martin’s Day, before the winter months began in earnest. A similar term that originated in America is “Indian Summer”.
- Ireland
In Ireland, on the eve of St. Martin’s Day, it is tradition to sacrifice a cockerel by bleeding it. The blood was collected and sprinkled on the four corners of the house. Also in Ireland, no wheel of any kind was to turn on St. Martin’s Day, because Martin was thrown into a mill stream and killed by the wheel and so it was not right to turn any kind of wheel on that day.
- Sicily
In Sicily, November is the winemaking season. On St. Martin’s Day Sicilians eat anise biscuits washed down with Moscato, Malvasia or Passito. More precisely, the hard biscuits are dipped into the Moscato. l’Estate di San Martino (Saint Martin’s Summer) is the traditional Sicilian reference to a period of unseasonably warm weather in early to mid November. Saint Martin’s Day is celebrated in a special way in a village near Messina and at a monastery dedicated to him overlooking Palermo beyond Monreale.
- Latvia
Mārtiņi (Martin’s) is traditionally celebrated by Latvians on November 10, marking the end of the preparations for winter, such as salting meat and fish, storing the harvest and making preserves. Mārtiņi also marks the beginning of masquerading and sledding, among other winter activities.
- Malta
St. Martin’s Day (Jum San Martin in Maltese) is celebrated in Malta on the Sunday nearest to November 11. Children are given a bag full of fruits and sweets associated with the feast, known by the Maltese as Il-Borża ta’ San Martin, “St. Martin’s bag”.
This bag may include walnuts, hazelnuts, almonds, chestnuts, dried or processed figs, seasonal fruit (like oranges, tangerines, apples and pomegranates) and “Saint Martin’s bread roll” (Maltese: Ħobża ta’ San Martin). In old days, nuts were used by the children in their games.
There is a traditional rhyme associated with this custom:
Ġewż, Lewż, Qastan, Tin
Kemm inħobbu lil San Martin.
Walnuts, Almonds, Chestnuts, Figs
I love Saint Martin so much.
A feast is celebrated in the village of Baħrija on the outskirts of Rabat (Malta), including a procession led by the statue of Saint Martin. There is also a fair, and a show for local animals. San Anton School, a private school on the island, organises a walk to and from a cave especially associated with Martin in remembrance of the day.
- Netherlands
The day is celebrated on the evening of the 11th of November (the day Saint Martin died), where he is known as Sint-Maarten. As soon it gets dark, children up to the age of 11 or 12 (primary school age) go door to door with hand-crafted lanterns made of hollowed-out sugar beet or, more recently, paper, singing songs such as “Sinte Sinte Maarten,” hoping to receive candy in return, similar to Halloween.
In the past, poor people would visit farms on the 11th of November, to get food for the winter. In the 1600’s, the city of Amsterdam held boat races. 400 to 500 light craft, both rowing boats and sailboats, took part under the eyes of a vast crowd on the banks.
- Poland
St. Martin’s Day is celebrated mainly in the city of Poznań. On November 11, the people of Poznań buy and eat considerable amounts of “Rogale” (pronounced Ro-gah-leh), locally produced croissants, made specially for this occasion, filled with almond paste with poppy seeds, so-called “Rogal świętomarciński” or Martin Croissants or St. Martin Croissants.
Legend has it this centuries-old tradition commemorates a Poznań baker’s dream. His nighttime reveries had St. Martin entering the city on a white horse that lost its golden horseshoe. The very next morning, the baker whipped up horseshoe-shaped croissants filled with almonds, white poppy seeds and nuts, and gave them to the poor.
In recent years, competition amongst local bakeries has become fierce for producing the best “Rogale,” and very often bakeries proudly display a certificate of compliance with authentic, traditional recipes. Poznanians celebrate with a feast, specially organised by the city. There are different concerts, a St. Martin’s parade and a fireworks show.
- Portugal
In Portugal, St. Martin’s Day is commonly associated with the celebration of the maturation of the year’s wine, being traditionally the first day when the new wine can be tasted.
It is celebrated, traditionally around a bonfire, eating the magusto, chestnuts roasted under the embers of the bonfire (sometimes dry figs and walnuts), and drinking a local light alcoholic beverage called água-pé (literally “foot water”, made by adding water to the pomace left after the juice is pressed out of the grapes for wine – traditionally by stomping on them in vats with bare feet, and letting it ferment for several days), or the stronger jeropiga (a sweet liquor obtained in a very similar fashion, with aguardente added to the water). Água-pé, though no longer available for sale in supermarkets and similar outlets (it is officially banned for sale in Portugal), is still generally available in small local shops from domestic production.
Leite de Vasconcelos regarded the magusto as the vestige of an ancient sacrifice to honor the dead and stated that it was tradition in Barqueiros to prepare, at midnight, a table with chestnuts for the deceased family members to eat. The people also mask their faces with the dark wood ashes from the bonfire. A typical Portuguese saying related to Saint Martin’s Day:
É dia de São Martinho;
comem-se castanhas, prova-se o vinho.
It is St. Martin’s Day,
we’ll eat chestnuts, we’ll taste the wine.
This period is also quite popular because of the usual good weather period that occurs in Portugal in this time of year, called Verão de São Martinho (St. Martin’s Summer). It is frequently tied to the legend since Portuguese versions of St. Martin’s legend usually replace the snowstorm with rain (because snow is not frequent in most parts of Portugal, while rain is common at that time of the year) and have Jesus bringing the end of it, thus making the “summer” a gift from God.
- Spain
In Spain, St. Martin’s Day is the traditional day for slaughtering fattened pigs for the winter. This tradition has given way to the popular saying “A cada cerdo le llega su San Martín”, which translates as “Every pig gets its St Martin.” The phrase is used to indicate that wrongdoers eventually get their comeuppance.
- St. Maarten / St. Martin
In Sint Maarten, November 11 is St. Martin’s Day, not because of the same traditions as in other countries but that’s the date when the island was discovered by Christopher Columbus, in 1493. It is a public holiday on both sides to commemorate this event. Celebrations highlight tradition music, culture, and food.
- Sweden
St Martin’s Day was an important medieval autumn feast, and the custom of eating goose spread to Sweden from France. In early November, geese are ready for slaughter, and on St. Martin’s Eve, November 10, it is time for the traditional dinner of roast goose.
The custom is particularly popular in Skåne in southern Sweden, where goose farming has long been practiced, but it has gradually spread northwards. A proper goose dinner also includes apple charlotte.
- Switzerland
Its celebration has mainly remained a tradition in the Swiss Catholic region of the Ajoie in the canton of Jura. The traditional gargantuan feast, the Repas du Saint Martin, includes all the parts of freshly butchered pigs, accompanied by shots of Damassine, and lasting for at least 5 hours.
- United States
In the United States St. Martin’s Day celebrations are uncommon, and when they do happen, reflect the cultural heritage of a local community.
Many German restaurants feature a traditional menu with goose and gluhwein (a mulled red wine). St. Paul, Minnesota celebrates with a traditional lantern procession around Rice Park. The evening includes German treats and traditions that highlight the season of giving. In Dayton, Ohio the Dayton Liederkranz-Turner organization hosts a St. Martin’s Family Celebration on the weekend before with an evening lantern parade to the singing of St. Martin’s carols, followed by a bonfire.
- Other customs
The Auvergne region of central France traditionally hosts horse fairs on St. Martin’s Day.
Source: Wikipedia
 July 9th is the Day of Unn the Wise person. Also known as Aud the Deep-Minded, Unn was a great matriarch who established dynasties in the islands Orcadas, Feroe and Iceland.
July 9th is the Day of Unn the Wise person. Also known as Aud the Deep-Minded, Unn was a great matriarch who established dynasties in the islands Orcadas, Feroe and Iceland.
Example to follow:
Make our own families grow strong, maintain the memory and traditions of our alive ancestors. Remember the great women of your own clan on this Day of Remembrance for Unn the Deep Minded.
About Unn:
Unn was a powerful figure from the Laxdaela Saga who emigrated to Scotland to avoid the hostility of King Harald Finehair. She was the second daughter of Ketill Flatnose, a Norwegian hersir, and Yngvid Ketilsdóttir, daughter of Ketill Wether, a hersir from Ringarike. Unn married Olaf the White (Oleif), son of King Ingjald, who had named himself King of Dublin after going on voyages to Britain and then conquering the shire of Dublin. They had a son named Thorstein the Red
She established dynasties in the Orkney and Faroe Islands by carefully marrying off her grand daughters. Unn then set off for Iceland.
On her ship were twenty men, all of whom were free, but she was still the leader of them, proving that she was respected, but also that she was strong-willed enough to command a ship alone without the help of a man. In addition to the crew, there many other men on her ship, prisoners from Viking raids near and around Britain. They all came from good families, and were called bondsmen. Unn gave these men their freedom once they were in Iceland, making them freed-men, a class between slave and free, where they were not owned, but did not have all the rights of a free man. She also gave them all a great deal of land to farm on and make a living.
As a settler in Iceland she continued to exhibit all those traits which were her hallmark-strong will, a determination to control, dignity, and a noble character. In the last days of her life, she established a mighty line choosing one of her grandsons as her heir. She died during his wedding celebration, presumably accomplishing her goals and working out her destiny in this life. She received a typical Nordic ship burial, surrounded by her treasure and her reputation for great deeds.
Note:
In some pagan calendars this is shown of “Day of Un the Wise Person” which is a misprint.
Source: Asatru.org
- Themes: Health; Kinship; Change; Opportunity
- Symbols: Beans; Pork
- Presiding Goddess: Carna
About Carna:
Goddess of protection, and of health and well-being of humans, especially small children. She presided over the intestines, heart, and other human organs. Some scholars have described Carna as being a Goddess of good digestion.
When parents appealed to Carna, this Goddess would enter the home and perform certain rites to bar a strix from entering the house. The strix was sort of a supernatural screech owl. If this evil creature could, it would fly in at night and eat a sleeping child’s intestines so the child would not get good nourishment and waste away.
To do today:
Romans traditionally gathered with their family on this day, offering Carna beans and pork to thank her for continued good health. This translates into a meal of pork, beans, and bacon to internalize her well-being! If you’re a vegetarian, just stick with the beans.
To get Carna’s assistance in getting an opportunity to open up, try this bit of sympathetic magic: Take any bean and go to your door. Stand before the door and say:
Carna, help this magic begin;
my future turns on your hinge.
Open the way, starting today!
Open the door as you say “open the way” and put the bean outside in a safe place to draw Carna’s opportunities to you.
To permanently close a chapter in your life, just alter the spell a bit. This time begin with the door open, saying:
Carna, help me leave the past behind;
by this spell this situation bind.
Away it goes, the door is closed!
Put the bean outside the door and close it as you say “the door is closed,” leaving the problem outside your life.
From: 365 Goddess
and The Goddess Dictionary
Sham el-Nisim is an Egyptian national holiday marking the beginning of spring. It always falls on Easter Monday, the day after the Eastern Christian Easter (following the custom of the largest Christian denomination in the country, the Coptic Orthodox Church).
Despite the Christian-related date, the holiday is celebrated by Egyptians of all religions, so it is considered a national festival, rather than a religious one. The main features of the festival are:
- People spend all day out picnicking in any space of green, public gardens, on the Nile, or at the zoo.
Traditional food eaten on this day consists mainly of fesikh (a fermented, salted and dried grey mullet), lettuce, scallions or green onions, tirmis, and colored boiled eggs.
The name of the holiday is derived from the Egyptian name of the Harvest Season, known as Shemu, which means a day of creation. According to annals written by Plutarch during the 1st century AD, the Ancient Egyptians used to offer salted fish, lettuce, and onions to their deities on this day.
After the Christianization of Egypt, the festival became associated with the other Christian spring festival, Easter. Over time, Shemu morphed into its current form and its current date, and by the time of the Islamic conquest of Egypt, the holiday was settled on Easter Monday. The Islamic calendar being lunar and thus unfixed relative to the solar year, the date of Sham el-Nessim remained on the Christian-linked date.
As Egypt became Arabized, the term Shemu found a rough phono-semantic match in Sham el-Nessim, or “Smelling/Taking In of the Zephyrs,” which fairly accurately represents the way in which Egyptians celebrate the holiday.
In his book, Manners and Customs of the Modern Egyptians, Edward William Lane wrote in 1834:
A custom termed ‘Shemm en-Nessem’ (or the Smelling of the Zephyr) is observed on the first day of the Khamaseen. Early in the morning of this day, many persons, especially women, break an onion, and smell it; and in the course of the forenoon many of the citizens of Cairo ride or walk a little way into the country, or go in boats, generally northward, to take the air, or, as they term it, smell the air, which on that day they believe to have a wonderfully beneficial effect. The greater number dine in the country or on the river. This year they were treated with a violent hot wind, accompanied by clouds of dust, instead of the neseem; but considerable numbers, notwithstanding, went out to ‘smell’ it.
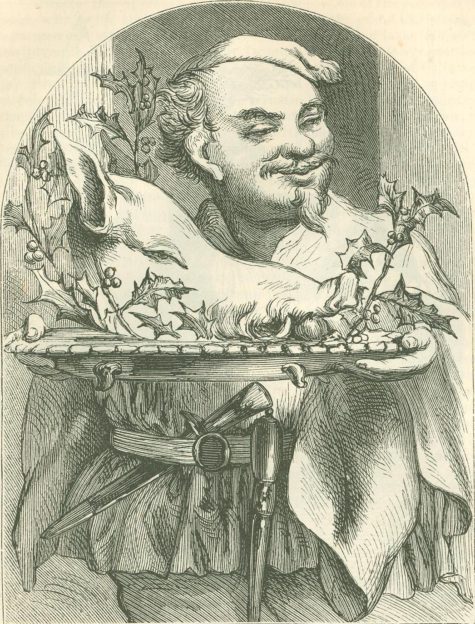
The sixth day of Christmas (Dec 30) is the day of “Bringing in the Boar.” Two traditions honor the importance of the boar at Solstice tide. In Scandinavia, Frey, the god of sunshine, rode across the sky on his golden-bristled boar. Gulli-burstin, who was seen as a solar image, his spikes representing the rays of the sun.
In the ancient Norse tradition, the intention was to gain favor from Frey in the new year. The boar’s head with an apple in his mouth was carried into the banquet hall on a gold or silver dish to the sounds of trumpets and the songs of minstrels.
In Scandinavia and England Saint Stephen (whose feast day is Dec 26) is shown as tending to horses and bringing a boar’s head to a Yuletide banquet. Christmas ham is an old tradition in Sweden and may have originated as a winter solstice boar sacrifice to Freyr.
Here’s a song from 1607:
The Boar is dead,
Lo, here is his head,
What man could have done more
Than his head off to strike,
Meleager like.
And bring it as I do before.
His living spoiled,
Where good men toiled,
Which makes kind Ceres sorry;
But now, dead and drawn,
he is very good brawn,
And we have brought it for ye.
Then set down the swineherd,
The foe of the vineyard,
Let Baccus crown his fall;
Let this boar’s head and mustard,
Stand for pig,goose and custard,
And so ye are welcome all.
From: The Winter Solstice and other sources.
Many countries in Europe celebrate the Feast of Sinterklaas, or St. Nicholas, on the eve of December 6. After dinner, families hunt for their presents, following clues in funny, anonymous poems. They also eat candies and cookies, especially spicy crispy ginger-cookie figures formed in a traditional wooden mold.
The legend of St. Nicholas is, like the lives of many saints, shrouded in mystery. We know that he was the bishop of Myra in Lycia, part of Asia Minor, during the fourth century. He is credited with saving three sisters from lives of ill repute by throwing bags of gold into their house (some say down the chimney, others say through the window) to provide for their dowries.
In many places in the United States and abroad, children still hang their stockings by the chimney or place their shoes by the window for St. Nicholas to fill them with presents and sweets on the eve of his feast day. He is considered the patron saint of children.
Source: Almanac.com