November Lore
According to astrological and lunar lore, there are best days for doing a variety of tasks. The best days listed here are based on both the phase of the moon and its position in the zodiac. Many people believe that if you do the tasks on the dates listed, you will get the best results possible.
November 1:
- Bake
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Potty Train a Child
- Wax Floors
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 2:
- Bake
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Potty Train a Child
- Wax Floors
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 3:
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Dig Holes
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Paint
- Potty Train a Child
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 4:
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Dig Holes
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Paint
- Potty Train a Child
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 5:
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Get Married
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Potty Train a Child
- Set Eggs
- Start Diet (to gain weight)
- Wax Floors
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 6:
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Get Married
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Potty Train a Child
- Start Diet (to gain weight)
- Wax Floors
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 7:
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Get Married
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Potty Train a Child
- Start Diet (to gain weight)
- Wax Floors
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 8:
- Bake
- Cut Firewood
- Dig Holes
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
November 9:
- Bake
- Cut Firewood
- Dig Holes
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
November 10:
- Advertise Something for Sale
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Get Married
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Paint
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Wax Floors
November 11:
- Advertise Something for Sale
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Get Married
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Paint
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Wax Floors
November 12:
- Advertise Something for Sale
- Ask For a Loan
- Dig Post Holes
- Make Jams and Jellies
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Paint
- Slaughter
- Transplant (seedlings and plants)
November 13:
- Cut Hair (to slow growth)
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Quit Smoking
- Set Eggs
- Slaughter
- Wash Wooden Floors
November 14:
- Cut Hair (to slow growth)
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Root Crops
- Quit Smoking
- Set Eggs
- Slaughter
- Wash Wooden Floors
November 15:
- Brew
- Can Fruits and Vegetables
- Hunting
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Flowers
- Plant Root Crops
- Plant Seed Beds
- Transplant (seedlings and plants)
November 16:
- Brew
- Can Fruits and Vegetables
- Hunting
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Flowers
- Plant Seed Beds
- Transplant (seedlings and plants)
November 17:
- Ask For a Loan
- Cut Hair (to slow growth)
- Demolition
- Dig Post Holes
- Dry Fruits and Vegetables
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Paint
- Pick Apples and Pears
- Quit Smoking
- Start Diet (to lose weight)
- Wash Wooden Floors
November 18:
- Ask For a Loan
- Cut Hair (to slow growth)
- Demolition
- Dig Post Holes
- Dry Fruits and Vegetables
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Paint
- Pick Apples and Pears
- Quit Smoking
- Start Diet (to lose weight)
- Wash Wooden Floors
November 19:
- Harvest
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Root Crops
- Quit Smoking
- Start Diet (to lose weight)
November 20:
- Harvest
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Root Crops
- Quit Smoking
- Start Diet (to lose weight)
November 21:
- Cut Hair (to slow growth)
- Get Married
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Flowers
November 22:
- Cut Hair (to slow growth)
- Get Married
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Flowers
November 23:
- Cut Hair (to slow growth)
- Get Married
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Flowers
November 24:
- Can Fruits and Vegetables
- Make Jams and Jellies
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Seed Beds
- Prune Trees
- Transplant (seedlings and plants)
November 25:
- Can Fruits and Vegetables
- Make Jams and Jellies
- Mow Grass (to slow growth)
- Plant Root Crops
- Plant Seed Beds
- Prune Trees
- Transplant (seedlings and plants)
November 26:
- Advertise Something for Sale
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Dig Holes
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Plant Root Crops
- Potty Train a Child
- Travel (for pleasure)
- Wash Windows
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 27:
- Advertise Something for Sale
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Dig Holes
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Potty Train a Child
- Travel (for pleasure)
- Wash Windows
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 28:
- Bake
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Potty Train a Child
- Wax Floors
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 29:
- Bake
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Cut Hair (to increase growth)
- Dig Holes
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Plant Above Ground Crops
- Potty Train a Child
- Wax Floors
- Wean a Baby or an Animal
November 30:
- Castrate Farm Animals
- Cut Firewood
- Dig Holes
- Kill Plant Pests
- Mow Grass (to increase growth)
- Paint
- Potty Train a Child
- Wean a Baby or an Animal :
Source: The Farmer’s Almanac
The Hunter’s Moon is so named because plenty of moonlight is ideal for hunters shooting migrating birds in Northern Europe. The name is also said to have been used by Native Americans as they tracked and killed their prey by autumn moonlight, stockpiling food for the winter ahead.
Traditional association with feasting:
In the northern hemisphere, the Hunter’s Moon appears in October or November, usually in October. Traditionally, it was a feast day in parts of western Europe and among some Native American tribes, called simply the Feast of the Hunter’s Moon, though the celebration had largely died out by the 18th century. There is a large historical reenactment by that name in Lafayette, Indiana during the early part of October 2010
Variation in time of moonrise:
In general, the moon rises about 50 minutes later each day, as it moves in orbit around Earth. All full moons rise around the time of sunset. The Harvest Moon (full moon closest to the Autumnal Equinox) and Hunter’s Moon are special because — as seen from the northern hemisphere — the time of moonrise on successive evenings is shorter than usual. The moon rises approximately 30 minutes later, from one night to the next, as seen from about 40 degrees N. latitude, for several evenings around the full Hunter’s or Harvest Moons.
Thus there is no long period of darkness between sunset and moonrise, around the time of these full moons. In times past, this feature of these autumn moons was said to help hunters tracking their prey (or, in the case of the Harvest Moon, farmers working in the fields). They could continue tracking their prey (or bringing in their crops) by moonlight even when the sun had gone down. Hence the name Hunter’s Moon.
The reason for the shorter-than-usual rising time between successive moon rises around the time of the Harvest and Hunter’s Moon is that the orbit of the Moon makes a narrow angle with respect to the horizon in the evening in autumn, leading the Moon to higher positions in the sky each successive day.
Brightness and distance:
The Hunter’s Moon is not brighter, smaller or yellower than during other times of the year, but all full moons have their own special characteristics, based primarily on the whereabouts of the ecliptic in the sky at the time of year that they are visible.
The full moons of September, October and November, as seen from the northern hemisphere — which correspond to the full moons of March, April and May as seen from the southern hemisphere — are well known in the folklore of the sky.
Since the Moon’s sidereal period differs from its synodic period, the perigee of the Moon (the point where it is closest to the Earth) does not stay in sync with the phases of the Moon. Thus the Hunter’s Moon does not correspond to any special timing of the Moon’s distance from the Earth. This is why the Hunter’s Moon is not, in general, brighter than any other regular full moon.
Source: Wikipedia
Eriskegal, great black mother of the House of Dust,
you who wait at the end of every life,
cast your dim black gaze upon the just
and, blinking once, give them rebirth.
While November is the eleventh month on modern calendars, it was once the ninth, as evidenced by the Latin number novem. In the United States, November contains one of the oldest national holidays – Thanksgiving.
Actually, festivals of gratitude combine with late harvest festivals in many parts of the world; at this time people pray for divine providence and give thanks for the earth’s bounty. Other predominant festivals during early winter months include commemorative rites for the dead and rituals that protect individuals or whole communities from evil influences.
For people living in four-season climates, the snows begin to accumulate and winter winds decorate the windows with frosty reminders of the outside chill. Because of this, magic for continued health is fitting during November, as are spells and charms for protection.
Wintery months also seem to be a time for introspection – to us divination tools for foresight and preparation, to seek guidance within, and to ask the Goddess for a special spiritual vision to carry us through the last months of the year.
Source: 365 Goddess
Image from: 2008 Witches Calendar
What follows is a list (in alphabetical order) of the names given to the November moon. Also listed is the tradition and/or origin of that moon name:
- All Gathered Moon ~San Juan, Native American
- Beaver Moon, ~Algonquin, Native American, Colonial
- Corn Harvest Moon ~Taos
- Dark Moon ~other
- Dead Moon ~Janic (dark)
- Deer Antler Shedding Moon ~other
- Deer Rutting Moon ~Cheyenne
- Falling Leaves Moon ~Sioux
- Fog Moon ~other
- Fledgling Raptor Moon ~Hopi
- Freezing River Moon ~Arapaho
- Frosty Moon ~Algonquin, Native American, Colonial
- Geese Going Moon ~Kiowa
- Itartoryuk Moon ~Inuit
- Mad Moon ~other
- Mourning Moon ~Janic (full)
- Oak Moon ~other
- Poverty Moon ~Mohawk
- Snow Moon ~Mediaeval English
- Snowy Morning Mountains Moon ~Wishram
- Storm Moon ~other
- Trading Moon ~Cherokee
- Tree Moon ~Neo Pagan
Source: Everything Under The Moon
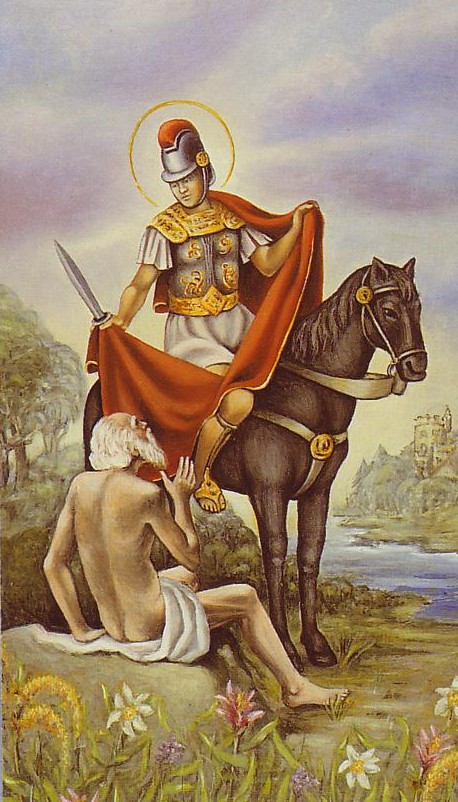
Saint Martin’s Day, also known as the Feast of Saint Martin, Martinstag or Martinmas, as well as Old Halloween and Old Hallowmas Eve, is the feast day of Saint Martin of Tours (Martin le Miséricordieux) and is celebrated on November 11 each year. This is the time when autumn wheat seeding was completed, and the annual slaughter of fattened cattle produced “Martinmas beef”. Historically, hiring fairs were held where farm laborers would seek new posts.
Saint Martin of Tours started out as a Roman soldier then was baptized as an adult and became a monk. It is understood that he was a kind man who led a quiet and simple life. The best known legend of his life is that he once cut his cloak in half to share with a beggar during a snowstorm, to save the beggar from dying from the cold. That night he dreamed that Jesus was wearing the half-cloak. Martin heard Jesus say to the angels, “Here is Martin, the Roman soldier who is now baptized; he has clothed me.”
St. Martin was known as friend of the children and patron of the poor. This holiday originated in France, then spread to the Low Countries, the British Isles, Germany, Scandinavia, and Eastern Europe. It celebrates the end of the agrarian year and the end of the harvest.
Bishop Perpetuus of Tours, who died in 490, ordered fasting three days a week from the day after Saint Martin’s Day (11 November). In the 6th century, local councils required fasting on all days except Saturdays and Sundays from Saint Martin’s Day to Epiphany (the Feast of the Three Wise Men and the star, c.f. Matthew 2: 1-12) on January 6, a period of 56 days, but of 40 days fasting, like the fast of Lent. It was therefore called Quadragesima Sancti Martini (Saint Martin’s Lent). This period of fasting was later shortened and called “Advent” by the Church.
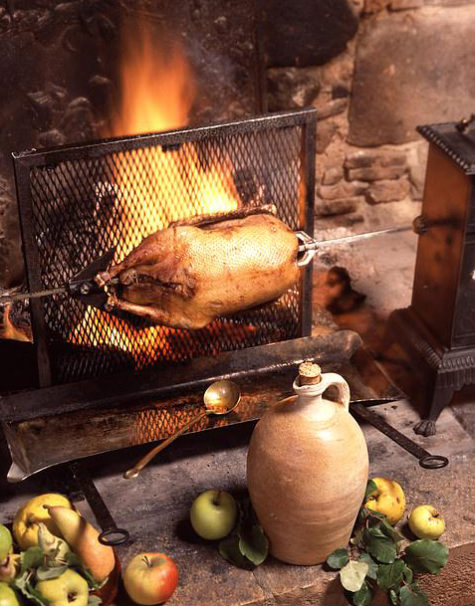
The goose became a symbol of St. Martin of Tours because of a legend that when trying to avoid being ordained bishop he had hidden in a goose pen, where he was betrayed by the cackling of the geese. St. Martin’s feast day falls in November, when geese are ready for killing.
St. Martin’s Day was an important medieval autumn feast, and the custom of eating goose spread to Sweden from France. It was primarily observed by the craftsmen and noblemen of the towns. In the peasant community, not everyone could afford to eat goose, so many ate duck or hen instead.
Martinmas
Martinmas literally means “Mass of Martin”, or the day when Catholics celebrate the Holy Catholic Mass which honors St. Martin in a special way.
Martinmas, as a date on the calendar, has two meanings: in the agricultural calendar it marks the beginning of the natural winter, but in the economic calendar it is seen as the end of autumn. The feast coincides not only with the end of the Octave of All Saints, but with harvest-time, the time when newly produced wine is ready for drinking, and the end of winter preparations, including the butchering of animals.
An old English saying is “His Martinmas will come as it does to every hog,” meaning “he will get his comeuppance” or “everyone must die”. Because of this, St. Martin’s Feast is much like the American Thanksgiving – a celebration of the earth’s bounty. Because it also comes before the penitential season of Advent, it is seen as a mini “carnivale”, with all the feasting and bonfires.
As at Michaelmas on 29 September, goose is eaten in most places. Following these holidays, women traditionally moved their work indoors for the winter, while men would proceed to work in the forests.
In some countries, Martinmas celebrations begin at the eleventh minute of the eleventh hour of this eleventh day of the eleventh month (that is, at 11:11 am on November 11). In others, the festivities commence on St. Martin’s Eve (that is, on November 10). Bonfires are built and children carry lanterns in the streets after dark, singing songs for which they are rewarded with candy.
It is also a day of wine tasting and drinking.
Celebrations around the world:
- Austria
“Martinloben” is celebrated as a collective festival. Events include art exhibitions, wine tastings, and live music. “Martinigansl” (roasted goose) is the traditional dish of the season. In Austria St. Martin’s Day is celebrated the same way as in Germany.The nights before and on the night of Nov. 11, children walk in processions carrying lanterns, which they made in school, and sing Martin songs.
- Belgium
The day is celebrated on the evening of November 11 in a small part of Belgium (mainly in the east of Flanders and around Ypres). Children go through the streets with paper lanterns and candles, and sing songs about St. Martin. Sometimes, a man dressed as St. Martin rides on a horse in front of the procession.
In some areas, there is a traditional goose meal, although in West Flanders there is no specific meal; in other areas it is more a day for children, with toys brought on the night of 10 to 11 November. In the east part of the Belgian province of West Flanders, especially around Ypres, children receive presents from either their friends or family as supposedly coming from St. Martin on November 11. In other areas it is customary that children receive gifts later in the year from either their friends or family as supposedly coming from Saint Nicholas on December 5 or 6 (called Sinterklaas in Belgium and the Netherlands) or Santa Claus on December 25.
In other areas, children go from door to door, singing traditional “Sinntemette” songs, sporting a hollow beetroot with a carved face and a candle inside. Later in the evening there is a bonfire where all of them gather. At the end the beetroots are thrown into the fire, and pancakes are being served.
- Croatia, Slovenia
In Croatia, St. Martin’s Day (Martinje, Martinovanje) marks the day when the must traditionally turns to wine. The must is usually considered impure and sinful, until it is baptized and turned into wine. The baptism is performed by someone who dresses up as a bishop and blesses the wine; this is usually done by the host. Another person is chosen as the godfather of the wine. The foods traditionally eaten on the day are goose and home-made or store bought mlinci.
The biggest event in Slovenia is the St. Martin’s Day celebration in Maribor which marks the symbolic winding up of all the wine growers’ endeavours. There is the ceremonial “christening” of the new wine, and the arrival of the Wine Queen. The square Trg Leona Štuklja is filled with musicians and stalls offering autumn produce and delicacies.
- Slovakia
In Slovakia, the Feast of St. Martin is like a “2nd Birthday” for those named after this saint. Small presents or money are common gifts for this special occasion. Tradition says that if it snows on the feast of St. Martin, November 11, then St. Martin came on a white horse and there will be snow on Christmas day. However, if it doesn’t snow on this day, then St. Martin came on a dark horse and it will not snow on Christmas.
- Czech Republic
A Czech proverb connected with the Feast of St. Martin – Martin přijíždí na bílém koni (trans. “Martin is coming on a white horse”) – signifies that the first half of November in the Czech Republic is the time when it often starts to snow. St. Martin’s Day is the traditional feast day in the run-up to Advent.
Roasted goose is usually found on restaurant menus, and the Czech version of Beaujolais nouveau, Svatomartinské víno, a young wine from the recent harvest, which has recently become more widely available and popular. Wine shops and restaurants around Prague pour the first of the St. Martin’s wines at 11:11 a.m. Many restaurants offer special menus for the day, featuring the traditional roast goose.
- Denmark
In Denmark, Mortensaften, meaning the evening of St. Martin, is celebrated with traditional dinners, while the day itself is rarely recognized. (Morten is the Danish vernacular form of Martin.) The background is the same legend as mentioned above, but nowadays the goose is most often replaced with a duck due to size, taste and/or cost.
- Estonia
In Estonia, Martinmas signifies the merging of Western European customs with local Balto-Finnic pagan traditions. It also contains elements of earlier worship of the dead as well as a certain year-end celebration that predates Christianity. For centuries mardipäev (Martinmas) has been one of the most important and cherished days in the Estonian folk calendar. It remains popular today, especially among young people and the rural population. Martinmas celebrates the end of the agrarian year and the beginning of the winter period.
Among Estonians, Martinmas also marks the end of the period of All Souls, as well as the autumn period in the Estonian popular calendar when the souls of ancestors were worshiped, a period that lasted from November 1 to Martinmas (November 11). On this day children disguise themselves as men and go from door to door, singing songs and telling jokes to receive sweets.
In Southern Estonia, November is called Märtekuu after St. Martin’s Day.
- Germany
A widespread custom in Germany is bonfires on St. Martin’s eve, called “Martinsfeuer.” In recent years, the processions that accompany those fires have been spread over almost a fortnight before Martinmas. At one time, the Rhine River valley would be lined with fires on the eve of Martinmas. In the Rhineland region, Martin’s day is celebrated traditionally with a get-together during which a roasted suckling pig is shared with the neighbors.
The nights before and on the night of Nov. 11, children walk in processions carrying lanterns, which they made in school, and sing Martin songs. Usually, the walk starts at a church and goes to a public square. A man on horseback dressed like St. Martin accompanies the children. When they reach the square, Martin’s bonfire is lit and Martin’s pretzels are distributed.
In some regions of Germany (e.g. Rhineland or Bergisches Land) in a separate procession the children also go from house to house with their lanterns, sing songs and get candy in return.
The origin of the procession of lanterns is unclear. To some, it is a substitute for the St. Martin bonfire, which is still lit in a few cities and villages throughout Europe. It formerly symbolized the light that holiness brings to the darkness, just as St. Martin brought hope to the poor through his good deeds. Even though the tradition of the large, crackling fire is gradually being lost, the procession of lanterns is still practiced.
The tradition of the St. Martin’s goose or “Martinsgans”, which is typically served on the evening of St. Martin’s feast day following the procession of lanterns, most likely evolved from the well-known legend of St. Martin and the geese. “Martinsgans” is usually served in restaurants, roasted, with red cabbage and dumplings.
In some regions of Germany, the traditional sweet of Martinmas is “Martinshörnchen”, a pastry shaped in the form of a croissant, which recalls both the hooves of St. Martin’s horse and, by being the half of a pretzel, the parting of his mantle. In parts of western Germany these pastries are instead shaped like men (Stutenkerl or Weckmänner).
- Great Britain
In the United Kingdom, St. Martin’s Day is known as Martinmas (or sometimes Martlemass). It is one of the term days in Scotland. Many schools celebrate St. Martin’s day. Many schools are also named after St. Martin.
Martlemass beef was from cattle slaughtered at Martinmas and salted or otherwise preserved for the winter. The now largely archaic term “St. Martin’s Summer” referred to the fact that in Britain people often believed there was a brief warm spell common around the time of St. Martin’s Day, before the winter months began in earnest. A similar term that originated in America is “Indian Summer”.
- Ireland
In Ireland, on the eve of St. Martin’s Day, it is tradition to sacrifice a cockerel by bleeding it. The blood was collected and sprinkled on the four corners of the house. Also in Ireland, no wheel of any kind was to turn on St. Martin’s Day, because Martin was thrown into a mill stream and killed by the wheel and so it was not right to turn any kind of wheel on that day.
- Sicily
In Sicily, November is the winemaking season. On St. Martin’s Day Sicilians eat anise biscuits washed down with Moscato, Malvasia or Passito. More precisely, the hard biscuits are dipped into the Moscato. l’Estate di San Martino (Saint Martin’s Summer) is the traditional Sicilian reference to a period of unseasonably warm weather in early to mid November. Saint Martin’s Day is celebrated in a special way in a village near Messina and at a monastery dedicated to him overlooking Palermo beyond Monreale.
- Latvia
Mārtiņi (Martin’s) is traditionally celebrated by Latvians on November 10, marking the end of the preparations for winter, such as salting meat and fish, storing the harvest and making preserves. Mārtiņi also marks the beginning of masquerading and sledding, among other winter activities.
- Malta
St. Martin’s Day (Jum San Martin in Maltese) is celebrated in Malta on the Sunday nearest to November 11. Children are given a bag full of fruits and sweets associated with the feast, known by the Maltese as Il-Borża ta’ San Martin, “St. Martin’s bag”.
This bag may include walnuts, hazelnuts, almonds, chestnuts, dried or processed figs, seasonal fruit (like oranges, tangerines, apples and pomegranates) and “Saint Martin’s bread roll” (Maltese: Ħobża ta’ San Martin). In old days, nuts were used by the children in their games.
There is a traditional rhyme associated with this custom:
Ġewż, Lewż, Qastan, Tin
Kemm inħobbu lil San Martin.
Walnuts, Almonds, Chestnuts, Figs
I love Saint Martin so much.
A feast is celebrated in the village of Baħrija on the outskirts of Rabat (Malta), including a procession led by the statue of Saint Martin. There is also a fair, and a show for local animals. San Anton School, a private school on the island, organises a walk to and from a cave especially associated with Martin in remembrance of the day.
- Netherlands
The day is celebrated on the evening of the 11th of November (the day Saint Martin died), where he is known as Sint-Maarten. As soon it gets dark, children up to the age of 11 or 12 (primary school age) go door to door with hand-crafted lanterns made of hollowed-out sugar beet or, more recently, paper, singing songs such as “Sinte Sinte Maarten,” hoping to receive candy in return, similar to Halloween.
In the past, poor people would visit farms on the 11th of November, to get food for the winter. In the 1600’s, the city of Amsterdam held boat races. 400 to 500 light craft, both rowing boats and sailboats, took part under the eyes of a vast crowd on the banks.
- Poland
St. Martin’s Day is celebrated mainly in the city of Poznań. On November 11, the people of Poznań buy and eat considerable amounts of “Rogale” (pronounced Ro-gah-leh), locally produced croissants, made specially for this occasion, filled with almond paste with poppy seeds, so-called “Rogal świętomarciński” or Martin Croissants or St. Martin Croissants.
Legend has it this centuries-old tradition commemorates a Poznań baker’s dream. His nighttime reveries had St. Martin entering the city on a white horse that lost its golden horseshoe. The very next morning, the baker whipped up horseshoe-shaped croissants filled with almonds, white poppy seeds and nuts, and gave them to the poor.
In recent years, competition amongst local bakeries has become fierce for producing the best “Rogale,” and very often bakeries proudly display a certificate of compliance with authentic, traditional recipes. Poznanians celebrate with a feast, specially organised by the city. There are different concerts, a St. Martin’s parade and a fireworks show.
- Portugal
In Portugal, St. Martin’s Day is commonly associated with the celebration of the maturation of the year’s wine, being traditionally the first day when the new wine can be tasted.
It is celebrated, traditionally around a bonfire, eating the magusto, chestnuts roasted under the embers of the bonfire (sometimes dry figs and walnuts), and drinking a local light alcoholic beverage called água-pé (literally “foot water”, made by adding water to the pomace left after the juice is pressed out of the grapes for wine – traditionally by stomping on them in vats with bare feet, and letting it ferment for several days), or the stronger jeropiga (a sweet liquor obtained in a very similar fashion, with aguardente added to the water). Água-pé, though no longer available for sale in supermarkets and similar outlets (it is officially banned for sale in Portugal), is still generally available in small local shops from domestic production.
Leite de Vasconcelos regarded the magusto as the vestige of an ancient sacrifice to honor the dead and stated that it was tradition in Barqueiros to prepare, at midnight, a table with chestnuts for the deceased family members to eat. The people also mask their faces with the dark wood ashes from the bonfire. A typical Portuguese saying related to Saint Martin’s Day:
É dia de São Martinho;
comem-se castanhas, prova-se o vinho.
It is St. Martin’s Day,
we’ll eat chestnuts, we’ll taste the wine.
This period is also quite popular because of the usual good weather period that occurs in Portugal in this time of year, called Verão de São Martinho (St. Martin’s Summer). It is frequently tied to the legend since Portuguese versions of St. Martin’s legend usually replace the snowstorm with rain (because snow is not frequent in most parts of Portugal, while rain is common at that time of the year) and have Jesus bringing the end of it, thus making the “summer” a gift from God.
- Spain
In Spain, St. Martin’s Day is the traditional day for slaughtering fattened pigs for the winter. This tradition has given way to the popular saying “A cada cerdo le llega su San Martín”, which translates as “Every pig gets its St Martin.” The phrase is used to indicate that wrongdoers eventually get their comeuppance.
- St. Maarten / St. Martin
In Sint Maarten, November 11 is St. Martin’s Day, not because of the same traditions as in other countries but that’s the date when the island was discovered by Christopher Columbus, in 1493. It is a public holiday on both sides to commemorate this event. Celebrations highlight tradition music, culture, and food.
- Sweden
St Martin’s Day was an important medieval autumn feast, and the custom of eating goose spread to Sweden from France. In early November, geese are ready for slaughter, and on St. Martin’s Eve, November 10, it is time for the traditional dinner of roast goose.
The custom is particularly popular in Skåne in southern Sweden, where goose farming has long been practiced, but it has gradually spread northwards. A proper goose dinner also includes apple charlotte.
- Switzerland
Its celebration has mainly remained a tradition in the Swiss Catholic region of the Ajoie in the canton of Jura. The traditional gargantuan feast, the Repas du Saint Martin, includes all the parts of freshly butchered pigs, accompanied by shots of Damassine, and lasting for at least 5 hours.
- United States
In the United States St. Martin’s Day celebrations are uncommon, and when they do happen, reflect the cultural heritage of a local community.
Many German restaurants feature a traditional menu with goose and gluhwein (a mulled red wine). St. Paul, Minnesota celebrates with a traditional lantern procession around Rice Park. The evening includes German treats and traditions that highlight the season of giving. In Dayton, Ohio the Dayton Liederkranz-Turner organization hosts a St. Martin’s Family Celebration on the weekend before with an evening lantern parade to the singing of St. Martin’s carols, followed by a bonfire.
- Other customs
The Auvergne region of central France traditionally hosts horse fairs on St. Martin’s Day.
Source: Wikipedia