Drinking
- Origin: Ireland
- Manifestation: Leprechauns are described as small wizened men wearing a shoemaker’s leather apron.
The stereotype of the Leprechaun involves lucky charms and pots of gold at the end of the rainbow. If captured by a human, they often grant three wishes in exchange for their freedom.
Leprechauns are highly commercially modified spirits; their image used to sell breakfast cereal, beer, and anything even remotely Irish. In recent years, Leprechauns, re-envisioned as “evil Fairies” have evolved into villains of horror movies; however this distorted image has no relation whatsoever to true Leprechauns who may be grouchy but are by no means vicious killers.
True Leprechauns are members of the Fairy folk, a type of sidhe. They are unusual because, in a realm dominated by females, Leprechauns are virtually exclusively male spirits.
The name Leprechaun derives from the Gaelic leigh brog “one shoemaker.” He is a cobbler, the only professional sidhe. While the other sidhe are out dancing and reveling, the Leprechaun is hard at work. He is, however, always seen working on only one shoe rather than a pair, which may be a shamanic reference.
References to shoes, especially one shoe, are often oblique references to shamanism. Ancient shamanic seances were often performed with one shoe on and one shoe off or featured dance steps that mimicked limping.
He works on shoes continually, with time off only for an occasional spree. The Leprechaun is fabulously wealthy: he buries his treasure in pots and is reputedly a skillful but not always nice practical joker. He may be invoked for financial aid.
Like other Irish fairies, Leprechauns may be derived from the Tuatha Dé Danann. Leprechaun-like creatures rarely appear in Irish mythology and only became prominent in later folklore.
- Interesting factoid: Leprechaunism is another name for Donohoe Syndrome, a rare genetic disorder characterized by delayed or diminished growth and facial features perceived as elfin.
According to Yeats, the solitary fairies, like the Leprechaun, wear red jackets, whereas the “trooping fairies” wear green. The Leprechaun’s jacket has seven rows of buttons with seven buttons to each row. On the western coast, he writes, the red jacket is covered by a frieze one, and in Ulster the creature wears a cocked hat, and when he is up to anything unusually mischievous, he leaps on to a wall and spins, balancing himself on the point of the hat with his heels in the air.
According to McAnally:
He is about three feet high, and is dressed in a little red jacket or roundabout, with red breeches buckled at the knee, gray or black stockings, and a hat, cocked in the style of a century ago, over a little, old, withered face. Round his neck is an Elizabethan ruff, and frills of lace are at his wrists. On the wild west coast, where the Atlantic winds bring almost constant rains, he dispenses with ruff and frills and wears a frieze overcoat over his pretty red suit, so that, unless on the lookout for the cocked hat, ye might pass a Leprechawn on the road and never know it’s himself that’s in it at all.
This dress could vary by region, however. In McAnally’s account there were differences between Leprechauns or Logherymans from different regions:
- The Northern Leprechaun or Logheryman wore a “military red coat and white breeches, with a broad-brimmed, high, pointed hat, on which he would sometimes stand upside down”.
- The Lurigadawne of Tipperary wore an “antique slashed jacket of red, with peaks all round and a jockey cap, also sporting a sword, which he uses as a magic wand”.
- The Luricawne of Kerry was a “fat, pursy little fellow whose jolly round face rivals in redness the cut-a-way jacket he wears, that always has seven rows of seven buttons in each row”.
- The Cluricawne of Monaghan wore “a swallow-tailed evening coat of red with green vest, white breeches, black stockings,” shiny shoes, and a “long cone hat without a brim,” sometimes used as a weapon.
In a poem entitled The Lepracaun; or, Fairy Shoemaker, 18th century Irish poet William Allingham describes the appearance of the Leprechaun as:
…A wrinkled, wizen’d, and bearded Elf,
Spectacles stuck on his pointed nose,
Silver buckles to his hose,
Leather apron — shoe in his lap…
The modern image of the Leprechaun sitting on a toadstool, having a red beard and green hat, etc. is clearly more modern invention or borrowed from other strands of European folklore. Films, television cartoons and advertising have popularized a specific image of Leprechauns which bears little resemblance to anything found in the cycles of Irish folklore. It can be considered that the popularized image of a Leprechaun is little more than a series of stereotypes based on derogatory 19th-century caricatures.
Catching A Leprechaun
Leprechaun traps are crafts made, typically in elementary school or by families with small children, to celebrate Saint Patrick’s Day. Leprechaun trapping can be compared to leaving cookies out for Santa Claus on Christmas Eve. The traps are set up the night before St. Patrick’s Day, and children awaken to discover signs that leprechauns have visited the trap.
The traps are typically made out of common household items that can be easily found or purchased. The traps are typically green and gold and feature the stereotypical leprechaun items: gold coins, rainbows, top hat and four leaf clover. A simple google search will reveal literally hundreds of DIY Leprechaun trap ideas.
According to the tradition, one must believe leprechauns are real to trap one. It is also believed that leprechauns love gold and trickery, and may steal or hide items unless captured, pleased, or scared away. Once trapped, Leprechauns may grant three wishes, and in many of the folklore stories, those lucky enough to catch one are tricked, and made foolish wishes which they lived to regret.
In most cases, children return to the trap with signs of a leprechaun visiting rather than a leprechaun itself. There might possibly be chocolate coins, and small treasures left in their bottom drawers.
If you Catch A Leprechaun
If you get lucky and manage to catch a leprechaun you need to be smarter than him or else you will be easily tricked which can have damaging results, never take your eye off him or he will vanish.
A captured leprechaun will grant you three wishes or a gold coin to bribe his way to freedom but this is when things can go terrible wrong if the wrong decisions are made.
- Use your 3 wishes wisely
Many of an Irish man who thought he could out smart an Irish leprechaun had selected the three wishes and would either go insane trying to think of what to wish for or their wishes would back fire with something bad happening.
One common story was of Seamus in County Mayo who wished to be the richest man on a tropical island. However, when his wish came true he suddenly realized that there were no shops or pubs on the island to spend his money or even people to talk with. Unfortunately Seamus became bored after a few hours on the Island and had to waste his third wish to return to Ireland. This could be how the phrase “luck of the Irish” originated from.
One of the biggest tips an Irish person can give anyone is to never listen to what the Irish leprechauns says, no matter what. The leprechauns are great mind players and will say anything to confuse you. You’ll make the wrong wishes, although he is smart he can be fooled.
- Never trust an Irish Leprechaun
Irish leprechauns are devious little creatures and will do anything to escape from man so they should never be trusted. Some say angry leprechauns are more common than a friendly one but this is very untrue as Irish leprechauns are very friendly but tend to dislike humans who always seem to chase them for wishes and pots of gold.
If you ever spot a leprechaun you may be better off to pass him by without taking notice, you can end up in more trouble than its worth if decide to chase them as the people of Ireland only know to well. Unfortunately with cities in Ireland expanding the poor wee leprechauns are being driven further underground away from man, taking their rainbows with them.
Sources:
- Encyclopedia of Spirits
- Wikipedia
- You’re Irish
Clurichauns may or may not be the same type of spirit as Leprechauns. If not, they are closely related. Like Leprechauns, Clurichans are virtually exclusively male. The Clurichaun may be the nocturnal form of the Leprechaun, out on a bender after a hard day’s work. Alternatively, some perceive Clurichauns to be Leprechauns lacking a work ethic.
Unlike hardworking, wealth-accumulating Leprechauns, Clurichauns spend all their time drinking. They are virtually always soused although they allegedly retain their good manners, unlike the reputedly sometimes surly Leprechaun. Clurichauns come out at night to drink, party and play pranks on people.
The folklorist Nicholas O’Kearney described the Clurichaun in 1855 as follows:
“ The Clobhair-ceann was another being of the same class: he was a jolly, red-faced, drunken little fellow, and was ever found in the cellars of the debauchee, Bacchus-like, astride of the wine-butt with a brimful tankard in hand, drinking and singing away merrily. Any wine cellar known to be haunted by this sprite was doomed to bring its owner to speedy ruin.”
Katharine Briggs stated that he was “a kind of buttery spirit, feasting himself in the cellars of drunkards or scaring dishonest servants who steal the wine.”
He is also described as a trickster and practical joker, and a disturber of order and quietness in a household, making noise day and night. Despite his often troublesome nature, the Clurichaun takes special care of the family to whom he has attached himself, endeavoring to protect their property and lives provided he is not interfered with. This dual nature makes him similar to the domestic hobgoblin.
Besides his love of drinking, the Clurichaun also enjoys pipe smoking, and the small disposable clay pipes known as “fairy pipes” that are often found while digging or plowing are said to belong to him. He also knows the secret of making beer from heather.
In olden days, many were butter thieves. They still like to raid the pantry.
The only occupation for which the Clurichaun displays enthusiasm is as guardian of wine and liquor cellars. The Clurichaun will protect your cellar from thieves and can allegedly prevent wine from spoiling and bottles from breaking or leaking. Simply request his presence and explicitly leave him a sample of whatever you have in stock. Leave him offerings on a regular basis lest he decide to begin serving himself. (He may anyway.)
The Clurichaun is sometimes portrayed carrying a jug of ale or wearing a leather apron with hammer in hand, whistling as he works. He also carries a magical purse (or sometimes a pewter beggars cup) with varying properties. It may contain a shilling (known as the “lucky shilling” or spre na skillenagh) that always returns to the purse no matter how often it is spent, or it may always be full of money, and for this reason mortals will often try to capture the Clurichaun . Even if he is caught he has the power to vanish if he can make his captor look away even for an instant.
He frequently carries two such purses, one containing the magic shilling and the other containing a normal copper coin, and if captured he will present the latter before vanishing. Like the Leprechaun he is sometimes said to have knowledge of hidden treasure and can be forced to reveal its location. In such instances one of his tricks is to create the illusion of multiple treasure markers so that the seeker will not know its exact whereabouts.
Clurichaun Stories
In the folktale “The Haunted Cellar”, recorded by Thomas Crofton Croker in 1825, a Clurichaun named Naggeneen haunts the wine cellar of an Irish lord, drinking everything in sight and playing frightening pranks on the servants.
He is described as a little man measuring six inches in height with a face like a withered apple. He has twinkling eyes and a nose that is red and purple from heavy drinking. He wears a red nightcap, a short leather apron, light blue stockings, and shoes with large silver buckles. When he is discovered by the master of the house, Naggeneen talks him out of moving elsewhere by implying that he would simply move with him.
Other descriptions have him wearing red like other solitary fairies.
In another tale, “Master and Man”, a young man named Billy Mac Daniel is on his way home one winter night when he is offered a glass of liquor by a Clurichaun to warm himself. He takes the drink but when he refuses to pay for it he is compelled by the Clurichaun to serve him for seven years and a day. Billy, however, is eventually able to break his servitude by invoking the blessing of God.
In this story, the Clurichaun is able to pass through keyholes to invade homes and wine cellars and can transform bog rushes into horses to be used as mounts. Clurichauns can also fly through the air on rushes similar to witches and their broomsticks.
Sources:
- Encyclopedia of Spirits
- Wikipedia
- Titles: Master of the Cemetery, Lord of the Dead
- Also known as: Bawon, Samedi, Bawon Sanmdi, Baron Saturday, Baron Sandi
- Colors: Black, also red and purple
- Day: Saturday
- Numbers: 3, 7, 21
- Classification: Lwa
- Consort: Madame Brigitte (Maman Brigitte)
- Venerated in: Haitian Vodou, Louisiana Voodoo, Folk Catholicism
- Feast: November 2
- Patronage: Death, tombs, gravestones, cemeteries, dead relatives, obscenities, healing, smoking, drinking, disruption, spirits
Baron Samedi is one of the loa of Haitian Vodou. He is the leader of the Barons and possibly the Gedes. He presides over a sprawling, confusing, complex clan of spirits. When people speak of the Baron, they tend to mean Baron Samedi. Baron Samedi literally means Baron Saturday, which may sound innocuous compared to Baron Cemetery, or Krininel, but Saturday was the one day when Christ was really truly dead, the day between the crucifixion on Friday and resurrection on Sunday. On Saturday, even Jesus must answer to the Baron, Lord of the Dead.
Baron Samedi is Grand Master of the Celestial Masonic Lodge of Vodou Spirits, a thirty-second degree initiated Mason. He is invoked to contact and communicate with the dead. He determines whether they can come visit or not. He may be petitioned to remove bothersome ghosts and invoked to ward off death.
He is noted for disruption, obscenity, debauchery, and having a particular fondness for tobacco and rum. Additionally, he is the loa of resurrection, and in the latter capacity he is often called upon for healing by those near or approaching death, as it is the only Baron who can accept an individual into the realm of the dead.
Baron Samedi spends most of his time in the invisible realm of vodou spirits. He is notorious for his outrageous behavior, swearing continuously and making filthy jokes to the other spirits. He is married to another powerful spirit known as Maman Brigitte, but often chases after mortal women. He loves smoking and drinking and is rarely seen without a cigar in his mouth or a glass of rum in his bony fingers.
Baron Samedi can usually be found at the crossroads between the worlds of the living and the dead. When someone dies, he digs their grave and greets their soul after they have been buried, leading them to the underworld.
He is a powerful healer and is especially sympathetic to terminally ill children. Baron Samedi rules the cemetery: no one can die until he gives permission for their grave to be dug. Baron Samedi is lewd, obscene, and vulgar, but he can be just and kind. He prefers that children live full lives before joining him in the cemetery.
Baron Samedi is the crossroads where sex and death meet. Spirit of the undying life-force, he may be petitioned for fertility. He is the guardian of ancestral knowledge and the link to your ancestral spirits. If one lens keeps popping out of your dark glasses, the Baron may be seeking your attention or offering his patronage.
Baron Samedi is syncretized to Jesus Christ as they share the symbol of the cross. It is possible that Baron Samedi’s associations with the cross may pre-date christianity. In Congolese cosmology, the cross is the symbol of the life cycle: death – birth – rebirth. He may also be syncretized to Saint Expedite, and with Saint Martin de Porres.
- Note:
Syncretized means to attempt to unite and harmonize especially without critical examination or logical unity.
Manifestations:
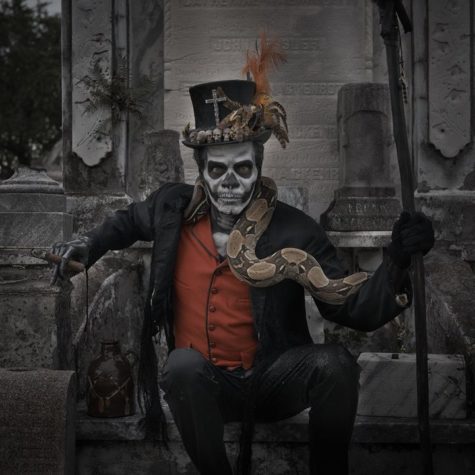
 Baron Samedi manifests as an older, dark-skinned man in formal attire, dressed completely in black. He wears a black top hat, black suit, and may be smoking one of his beloved cigars. He wears impenetrable black sunglasses.
Baron Samedi manifests as an older, dark-skinned man in formal attire, dressed completely in black. He wears a black top hat, black suit, and may be smoking one of his beloved cigars. He wears impenetrable black sunglasses.
- The glasses may be missing a lens because he possesses two kinds of vision: he simultaneously sees the realms of the living and the dead.
- Alternatively his glasses have but one lens because a penis has but one eye and the phallus is his attribute (and because he loves sexual humor and innuendo.)
He is usually depicted with a top hat, black tail coat, dark glasses, and cotton plugs in the nostrils, as if to resemble a corpse dressed and prepared for burial in the Haitian style. He has a white, frequently skull-like face (or actually has a skull for a face), and speaks in a nasally voice. The former President for Life of Haiti, François Duvalier, modeled his cult of personality on Baron Samedi; he was often seen speaking in a deep nasal tone and wearing dark glasses.
- Favored People
Children; women seeking to conceive; funeral workers; grave diggers; those whose work brings them into contact with death.
Connection to other loas:
Baron Samedi is the leader of the Guédé, loa with particular links to magic, ancestor worship and death. Samedi is a loa of the dead, along with Baron’s numerous other incarnations Baron Cimetière, Baron La Croix, and Baron Kriminel. These lesser spirits, all dressed like the Baron, are all as rude and crude, but not nearly as charming as their master. They help carry the dead to the underworld.
Working with Baron Samedi
- Iconography: Baron Samedi’s throne is a chair chained to a cross. Images of Darth Vader are supposed to represent him (or just to decorate his altar; he likes toys)
- Attributes: Coffin; phallus, skull and crossbones; shovel; grave; black sunglasses; cross
As well as being master of the dead, Baron Samedi is also a giver of life. He can cure any mortal of any disease or wound, if he thinks it is worthwhile. His powers are especially great when it comes to vodou curses and black magic. Even if somebody has been afflicted by a hex that brings them to the verge of death, they will not die if the Baron refuses to dig their grave. So long as this mighty spirit keeps them out of the ground, they are safe.
He also ensures that all corpses rot in the ground to stop any soul from being brought back as a brainless zombie. What he demands in return depends on his mood. Sometimes he is content with his followers wearing black, white or purple clothes or using sacred objects; he may simply ask for a small gift of cigars, rum, black coffee, grilled peanuts, or bread. But sometimes the Baron requires a vodou ceremony to help him cross over into this world.
- Offerings
Black coffee, plain bread, dry toast, roasted peanuts. He drinks rum in which twenty-one very hot peppers have been steeped. Cigars, cigarettes, dark sun glasses, Day of the Dead toys, the sexier and more macabre the better; raise a skull and crossbones pirate flag for him, beautiful wrought-iron crosses are crafted in his honor.
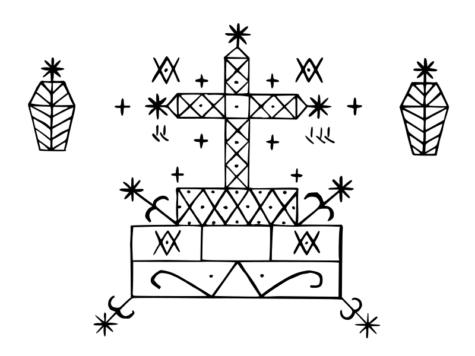
- Veve
The veve or symbol for Baron Samedi is as follows:
Sources: Wikipedia and Encyclopedia of Spirits
Bona Dea (“The Good Goddess”) was a divinity in ancient Roman religion. She was associated with chastity and fertility in women, healing, and the protection of the Roman state and people. According to Roman literary sources, she was brought from Magna Graecia at some time during the early or middle Republic, and was given her own state cult on the Aventine Hill.
Bona Dea was worshipped only by women. In fact, the presence of a man at rites in her honor were a sacrilige. May 1 was the annual, state-sponsored festival to Bona Dea at her temple. In early December, there was another private festival as well.
Her rites allowed women the use of strong wine and blood-sacrifice, things otherwise forbidden them by Roman tradition. Men were barred from her mysteries and the possession of her true name. Given that male authors had limited knowledge of her rites and attributes, ancient speculations about her identity abound, among them that she was an aspect of Terra, Ops, the Magna Mater, or Ceres, or a Latin form of Damia. Most often, she was identified as the wife, sister or daughter of the god Faunus, thus an equivalent or aspect of the nature-goddess Fauna, who could prophesy the fates of women.
The Good Goddess was a patron of the good of the earth and of chastity and fertility in women, she was invoked for healing and for freedom from slavery. Many of her worshippers were freed slaves and plebians, and many were women seeking aid in sickness or for fertility. She was also considered a protector from earthquakes.
Bona Dea was sometimes depicted with a scepter, vine leaves, wine, and a serpent, usually curled around her arm. Sometimes she was depicted seated, holding a cornucopia. Her image appeared on many coins.
The temple to Bona Dea in Rome stood over an overhanging rock, or cave, and both serpents and healing herbs are associated with the cave. The temple contained many kinds of healing herbs and snakes (both associated with medicine). Men were not allowed in her temple or at her festivals, nor were male animals.
The temple was decorated with vine-branches, and other plants and flowers (although myrtle was not permitted). Wine was served, but it was referred to as “milk” and the jar in which it was served, a “honey-pot.” A sow was sacrificed to her at the ritual.
Another ceremony was held in December in honor of the Bona Dea. The rites were conducted annually by the wife of the senior magistrate present in Rome in his home. She was assisted by the Vestal Virgins. The December rite was interesting because unlike the festival in May, it was not held in the goddess’ temple, not paid for by the state and the night of its celebration was not fixed. Unlike the May celebration, the December ceremony was an invitation only affair and pretty exclusive.
The celebrations for the Bona Dea seem to have been in the nature of a mystery cult. Men were strictly forbidden and the details that we have of the ceremony are from a late source, Macrobius. The worship seems to have been agricultural in origin and the careful exclusion of myrtle (associated with flagellation) may actually suggest origins as a purification ceremony.
In the year 62 BCE, the celebration was held in the home of Julius Caesar, then praetor and Pontifex Maximus, on December 3rd. His wife Pompeia and his mother, Aurelia, were in charge. A notorious Roman politician, Publius Clodius, dressed up as a woman and sneaked into the house. He was eventually caught by Caesar’s mother and kicked out. The ceremony had to be performed anew.
Caesar divorced his wife over it (claiming even she had to be above suspicion). Publius Clodius was sued and at his trial Cicero blew his alibi. The two became mortal enemies over the affair. The rites seemed to have fallen into disrepute over the events, and by the early empire, Juvenal suggested that it was nothing but a drunken orgy for girls.
Collected from various sources including: Women’s History, Ancient History, and Wikipedia
Dagda is the most prominent God of Celtic Mythology, leader of the Tuatha De Danann (Irish race of Gods of Mythology). He is identified with the Weish Gwydon and the Gallic Sucellos.
His titles and attributes:
- Mighty Red One
- Groat Knwdelle
- Ruler over Life and Death
- God of Time and Protector of Crops
- The Good God and Ollathir (All Father)
- God of Earth and Treaties
- Master of Magic
- Fearsome Warrior
Chief of the Tuatha Dé Daan, oldest of the Celtic deities, Dagda literally means “the good god.” What was his real name? That information may be reserved for initiates or he may be so old, no one knows any longer.
The Dagda is a spirit of magic and abundance. He is the tribal All Father, deity of the Druids, Lord of Regeneration, provider of plenty, Captain of Abundance. He is the Lord of New Grange. His children, Brigid and Angus Mac Og, are among the most powerful and beloved Irish deities. He plays the role of ideal father for his devotees.
The Dagda’s barrow (sidhe) features an inexhaustible supply of drink, three trees that always bear fruit, and a pig that is always alive, even though it’s slaughtered and consumed daily. He may be the prototype of the Grail King. The Romans identified him with Hercules.
The Dagda is the master of paradox. Incredibly wise and powerful, he’s uncouth and bumbling too. He’s an old, bald, fat, sloppy guy, but he’s a sex master too, a fertility spirit renowned for virility and sexual prowess. The Dagda engages in the Great Rite with great goddesses like the Morrigan and Boann.
- Mount: A black stallion named Ocean
- Sacred Day: On Samhain, the Dagda performs the Great Rite. On a day otherwise associated with death, the Dagda creates new life.
- Offerings: Oatmeal, porridge, mead, Irish whiskey, poteen
Manifestation:
A big, bald, bumbler with a beer belly; the Dagda wears a rustic tunic that no longer fits him. It’s too short for him, barely covering his buttocks and periodically exposing them. Don’t be fooled by his appearance. The Dagda only plays the fool; he’s brilliant, wise, and powerful. Furthermore, although it’s his posterior that’s mockingly discussed in myth, at least in the surviving ones recorded by Christian priests, tunics don’t only ride up in the back.
He was traditionally portrayed wearing a brown tunic that reached his hips, letting his huge penis drag while walking, a hooded cape that covered his shoulders and horse boots.
Dagda was commonly believed to be a crude and comical God. Some characteristics of The Good God, were his super strength, his insatiable need for women and food. He is a phallic deity, master of fertility and abundance. He was also a skilled artisan.
This God had various precious possessions:
- A cauldron with unlimited food supply called Undry.
- A living oak harp named Uaithne that he used to summon the seasons.
- An iron cub that could kill nine men with one side and bring them back to life with the other side.
- Three trees that always bear fruit.
- A pig that is always alive, even though it’s slaughtered and consumed daily.
The Dagda, a master harper, has a repertoire of magical songs:
- Those that make him invisible on the battlefield.
- Songs to seduce people into sex or foolish behavior, against their better judgment.
- And music of Sorrow, of Joy and Dreaming.