Wind
- Titles: Daughter of Nature, Goddess of Creation, Water Mother, Sky Mother
- Other Names: Luonnotar, Luonotar
- Origin: Finland
- Depicted as: Virgin floating on the sea
- Feast day: August 26
The name Ilmatar is derived from the Finnish word ilma, meaning “air,” and the suffix -tar, denoting a female spirit. Thus, her name literally means “female air spirit.” In the Kalevala she was also occasionally called Luonnotar,which means “female spirit of nature” (Finnish luonto, “nature”)
The story is as follows:
In the beginning, says the Kalevala, there was only Ilmatar, the void and a great deal of wind. She was alone in the beginning of time. She lived in the heavens, but eventually she grew restless and slipped into the vast cosmic sea. She floated and frolicked for centuries on this primordial ocean, counting rainbows and letting the wind play in her hair.
She began to long for a son.Her longing was so great that the East Wind itself took pity. She found herself buffeted and tossed by the wind’s tempestuous love-making until, exhausted, she could bear it no longer and collapsed. During this storm she became pregnant. And there, inside her, was conceived Vainamoinen, the child of the wind.
The goddess floated for centuries on this primordial ocean, unable to give birth because there was no land. She prayed constantly to the god Ukko, the highest of the gods, to help her. After seven centuries or so she began to give up hope, and Ukko took pity on her and sent a duck.
The poor bird was desperately looking for somewhere to land so she could make a nest and lay her eggs. When Ilmatar saw the bird’s predicament, she helpfully raised her knee and the bird came swooping down. Half a dozen cosmic eggs were laid, followed by an egg made of iron. The bird then gathered them all up, sat upon them and went to sleep.
Luonnotar sat and watched the bird eagerly, happy for something to finally be happening after centuries of loneliness and boredom. She became too excited, however, her leg began to heat up, she became extremely uncomfortable. Slowly, carefully, she began to stretch out her leg.. and slowly, inevitably, the seven eggs rolled off and fell majestically into the raging sea.
Now, cosmic eggs are delicate things, as soon as they fell into the waters, they broke open. Ilmatar watched in amazement as the broken shells of the eggs formed the heavens and the earth. The yolks became the sun, the whites the moon, and scattered fragments of the eggs transformed into the stars.
And thus the world was formed. As for the iron egg, the black yolk became a thundercloud.
Ilmatar was delighted with events, and busied herself shaping the lands and adding finishing touches. Even though dry land was now available, Ilmatar continued to carry the child within her for thirty summers while she finished her work. Eventually, she felt a stirring inside her. Vainamoinen had woken up after 30 years of being in the womb and was eager to see the new world. He had quite a struggle to get out, but he managed in the end and eventually, Ilmatar gave birth to Vainamoinen, a bouncing bonny old man, and the worlds first shaman, who then finished her creation.
Compiled from various sources
- Origin: Greece
- Festival Days: Jan 16 and 17 – Greek festival in which offerings were made to the Wind Gods of the Eight Directions
In ancient Greek religion and myth, the Anemoi (Greek: Ἄνεμοι, “Winds”) were wind gods who were each ascribed a cardinal direction from which their respective winds came, and were each associated with various seasons and weather conditions.
They were sometimes represented as mere gusts of wind, at other times were personified as winged men, and at still other times were depicted as horses kept in the stables of the storm god Aeolus, who provided Odysseus with the Anemoi in the Odyssey. The Spartans were reported to sacrifice a horse to the winds on Mount Taygetus. Astraeus, the astrological deity, and Eos/Aurora, the goddess of the dawn, were the parents of the Anemoi, according to the Greek poet Hesiod. The daughters of the Anemoi are the Aurae (wind nymphs).
According to Hesiod, the beneficial winds, Notus, Boreas, Argestes, and Zephyrus, were the sons of Astraeus and Eos, and the destructive ones, as Typhon, are said to be the sons of Typhoeus. Later, especially philosophical writers, endeavoured to define the winds more accurately, according to their places in the compass.
The Anemoi are divided into two groups:
- Anemoi Major
- Boreas: North Wind
- Eurus: East Wind
- Notus: South Wind
- Zephyr: West Wind
- Anemoi Minor
- Apeliotes: Southeast Wind
- Kaikias: Northeast Wind
- Livos (Lips): Southwest Wind
- Skiron (Skeiron): Northwest Wind
Of the four chief Anemoi, Boreas (Aquilo in Latin) was the north wind and bringer of cold winter air, Zephyrus (Favonius in Latin) was the west wind and bringer of light spring and early summer breezes, and Notos (Auster in Latin) was the south wind and bringer of the storms of late summer and autumn; Eurus, the southeast (or according to some, the east) wind, was not associated with any of the three Greek seasons, and is the only one of these four Anemoi not mentioned in Hesiod’s Theogony or in the Orphic Hymns.
Other Minor Wind Deities:
- Argestes “clearing”, a wind blowing from about the same direction as Skiron (Caurus), and probably another name for it
- Aparctias, sometimes called the north wind instead of Boreas
- Thrascias, the north-north-west wind (sometimes called in Latin Circius)
- Euronotus, the wind blowing from the direction, as its name suggests, between Euros and Notos, that is, a south-southeast wind (Euroauster to the Romans)
- Iapyx, the northwest wind about the same as Caurus. It was this wind, according to Virgil, that carried the fleeing Cleopatra home to Egypt after she was defeated at the battle of Actium.
- Libonotus, the south-southwest wind, known as Austro-Africus to the Romans
- Meses, another name for the north-west wind Skiron
- Olympias, apparently identified with Skiron/Argestes
- Phoenicias, another name for the southeast wind (“the one blowing from Phoenicia”, due to this land lying to the south-east of Greece)
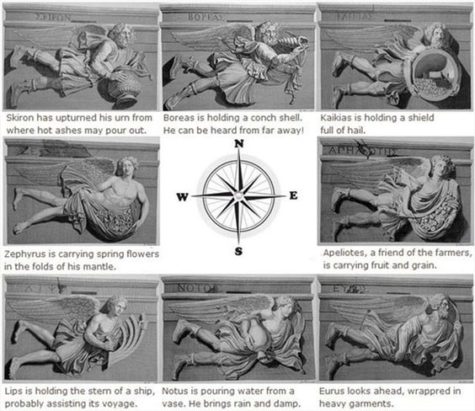
 The most remarkable monument representing the winds is the octagonal tower of Andronicus Cyrrhestes at Athens. Each of the eight sides of the monument represents one of the eight principal winds in a flying attitude.
The most remarkable monument representing the winds is the octagonal tower of Andronicus Cyrrhestes at Athens. Each of the eight sides of the monument represents one of the eight principal winds in a flying attitude.
A moveable Triton in the centre of the cupola pointed with his staff to the wind blowing at the time.
All these eight figures have wings at their shoulders, all are clothed, and the peculiarities of the winds are indicated by their bodies and various attributes.
This is how it looks today: