Antiseptic
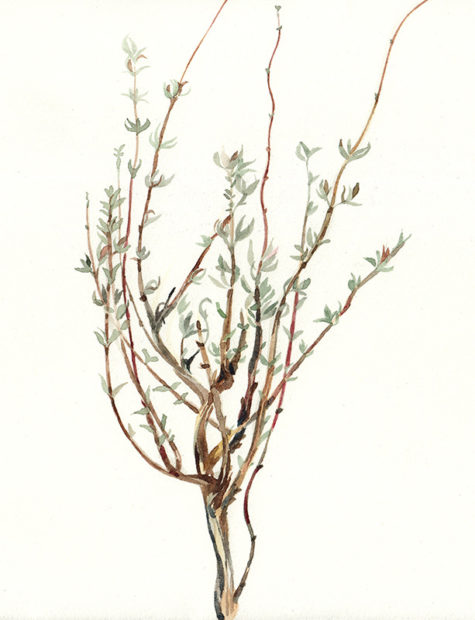
Mastic Thyme aka Spanish Marjoram
- Scientific Name: Thymus mastichina
- Common Name: Spanish Marjoram
- Plant Family: Lamiaceae or Labiatae
- Parts Used: Leaves, Flowers, Essential Oil
- Actions: Antiseptic, Deodorant, Disinfectant, Analgesic, Anti-inflammatory, Antibacterial
General Overview
Thymus mastichina is a very special thyme, native in the mountains of the Iberian Peninsula, Central Spain and Portugal. It is known by a number of different common names including Spanish Marjoram, Spanish Wood Marjoram, White Thyme, Wild Marjoram or Mastic Thyme. The leaves, and especially the essential oil contained in them, are strongly antiseptic, deodorant and disinfectant.
Thymus mastichina should not be confused with Marjoram also known as sweet Marjoram, knotted Marjoram and previously classed as Marjorana hortensis (Origanum majorana). Nor should it be confused with the Mastic Tree (Pistacia lentiscus).
As the name implies it grows primarily in Spain. Thymus mastichina produces tiny, oval-shaped, green leaves, which have an intense flavor. In its Spanish homeland it is used as a culinary herb for meat dishes, stews and sauces and because of its strong aroma has been commonly used in Andalucía to season and preserve olives.
Despite this fact, it is prized more for its essential oils than for its herbal properties. The plant has an herbaceous scent with eucalyptus-like overtones with a hint of a vanilla note, which, in aromatherapy, is used for its soothing, relaxing effect. It’s oil is pale orange to amber in color and has a distinctive eucalyptus like aroma. It is also considered to be especially beneficial in relaxing muscles.
Used fresh or in dried form, its leaves are used to make an herbal tea that is considered useful in treating sore throats, catarrh and colds. If preferred, the tea can be used to gargle with rather than ingested. Infusions are attributed curative or palliative properties of arthritis and rheumatism. Mastic Thyme, may be effective in protecting against colon cancer.
The Basics
The species name mastichina and the common name of Mastic Thyme derive from the Greek word massein, meaning ‘to chew’, or the verb mastichein meaning ‘to gnash the teeth’. It is the origin of the English word masticate.
Interestingly, the Mastic Tree is a small Mediterranean evergreen tree (Pistacia lentiscus) of the cashew family. The tree produces an aromatic, ivory-coloured resin, also known as mastic, is harvested as a spice from the cultivated mastic trees grown in the south of the Greek island of Chios in the Aegean Sea. Mastic resin is a relatively expensive kind of spice that has been used principally as a chewing gum. The flavor can be described as a strong, slightly smoky, resiny aroma.
Mastic Thyme produces tiny, oval-shaped, green leaves, which have an intense flavor. In its Spanish homeland it is used as a culinary herb for meat dishes, stews and sauces and because of its strong aroma has been commonly used in Andalucía to season and preserve olives.
Despite this fact, it is prized more for its essential oils than for its herbal properties. The plant has an herbaceous scent with eucalyptus-like overtones with a hint of a vanilla note, which, in aromatherapy, is used for its soothing, relaxing effect. It is also considered to be especially beneficial in relaxing muscles. The essential oil is most often found under the name: Spanish Marjoram.
Used fresh or in dried form, its leaves are used to make an herbal tea that is considered useful in treating sore throats, catarrh and colds. If preferred, the tea can be used to gargle with rather than ingested. Infusions are attributed curative or palliative properties of arthritis and rheumatism.
The leaves are used as a seasoning. They have a pungent eucalyptus-like aroma. If the leaves are to be dried, the plants should be harvested in early and late summer just before the flowers open and the leaves should be dried quickly. The plant is also the source of an essential oil, called “oil of marjoram” or “Spanish Marjoram”, that is used extensively as a flavoring for soups etc.
The essential oil obtained from the leaves is also used in perfumery, as a mouth wash, medicinally etc.
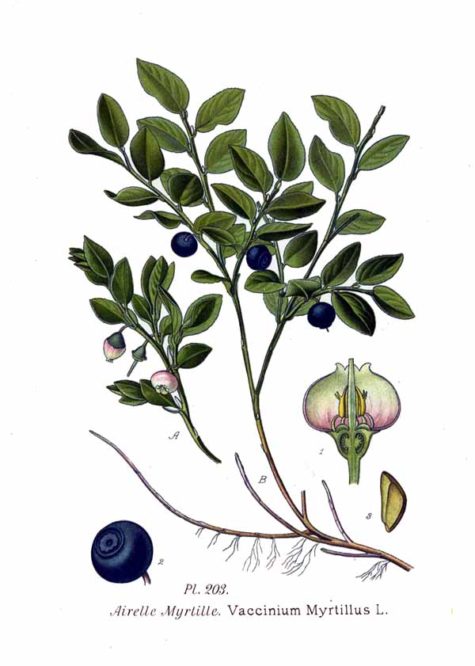
Bilberry
- Scientific Name: Vaccinium myrtillus
- Plant Family: N.O. Vacciniaceae
- Parts Used: The ripe fruit. The leaves.
- Actions: astringent, diuretic, tonic, antiseptic,antibacterial
Varieties:
- V. arboreum, or Farkleberry. This is the most astringent variety, and both berries and root-bark may be used internally for diarrhoea, chronic dysentery, etc. The infusion is valuable as a local application in sore throat, chronic ophthalmia, leucorrhoea, etc.
- V. resinosum, V. damusum, and V. gorymbosum have properties resembling those of V. myrtillus.
- The Bog Bilberry ( V. uliginosum) is a smaller, less erect plant, with round stems and untoothed leaves, greyish green beneath. Both flowers and berries are smaller than those of the common Bilberry. This kind is quite absent in the south and only to be found in mountain bogs and moist copses, in Scotland, Durham and Westmorland.
- The ‘Huckleberry’ of North America, so widely appreciated there, is our Bilberry – the name being an obvious corruption of ‘Whortleberry.’
Constituents: The leaves contain glucoquinones, which reduce the levels of sugar in the blood. The skin of the fruits contains anthocyanin and is specific in the treatment of hemeralopia (day-blindness). The fruit is a rich source of anthocyanosides, which have been shown experimentally to dilate the blood vessels.
The Basics:
Although often called huckleberry, the bilberry is more nearly related to the cranberry. Vaccinium myrtillus has been used for nearly 1,000 years in traditional European medicine. Bilberry fruits have been used in the traditional Austrian medicine internally (directly or as tea or liqueur) for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and diabetes. Herbal supplements of V. myrtillus (bilberry) on the market are used for circulatory problems, as vision aids, and to treat diarrhea and other conditions.
Bilberry is a well-known folk remedy for poor vision, especially for people who suffer from “night blindness,” that is, they have difficulty seeing in the dark. In fact, bilberry jam was given to Royal Air Force pilots who flew nighttime missions during World War II. It works by accelerating the regeneration of retinol purple, commonly known as visual purple, a substance that is required for good eyesight. European medical journals are filled with studies confirming bilberry’s positive effect on vision. Unfortunately, this herb has not received the attention it deserves in the American medical community so far.
Some people use bilberry for conditions of the heart and blood vessels including hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), varicose veins, decreased blood flow in the veins, and chest pain. Bilberry is also used for chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), hemorrhoids, diabetes, osteoarthritis, gout, skin infections, gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, kidney disease, and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
The dried leaves of bilberries are used in the treatment of a variety of complaints. A tea made from the dried leaves is strongly astringent, diuretic, tonic and an antiseptic for the urinary tract. It is also a remedy for diabetes if taken for a prolonged period. Another report says that the leaves can be helpful in pre-diabetic states but that they are not an alternative to conventional treatment. The leaves contain glucoquinones, which reduce the levels of sugar in the blood.
A decoction of the leaves or bark is applied locally in the treatment of ulcers and in ulceration of the mouth and throat. It is sometimes applied directly to the inside of the mouth for mild mouth and throat soreness. A distilled water made from the leaves is an excellent eyewash for soothing inflamed or sore eyes.
Whilst the fresh fruit has a slightly laxative effect upon the body, when dried it is astringent and is commonly used in the treatment of diarrhea etc. The dried fruit is also antibacterial and a decoction is useful for treating diarrhea in children. The skin of the fruits contains anthocyanin and is specific in the treatment of hemeralopia (day-blindness). The fruit is a rich source of anthocyanosides, which have been shown experimentally to dilate the blood vessels, this makes it a potentially valuable treatment for varicose veins, hemorrhoids and capillary fragility.
How does it work?
Bilberry contains chemicals called tannins that can help improve diarrhea, as well as mouth and throat irritation, by reducing swelling (inflammation). There is some evidence that the chemicals found in bilberry leaves can help lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Some researchers think that chemicals called flavonoids in bilberry leaf might also improve circulation in people with diabetes. Circulation problems can harm the retina of the eye. Continue reading
Peppermint
- Scientific Name: Mentha x piperita
- Plant Family: Labiatae
- Parts Used: Aerial parts
- Actions: Anodyne, Antiseptic, Antispasmodic, Carminative, Cholagogue, Diaphoretic, Refrigerant, Stomachic, Tonic. Vasodilator
- Constituents: Up to 2 % volatile oil containing menthol, menthone and jasmone; tannins, bitter principle
Variations:
There are several varieties of Peppermint. The two chief, the so-called ‘Black’ and ‘White’ mints are the ones extensively cultivated. Botanically there is little difference between them, but the stems and leaves of the ‘Black’ mint are tinged purplish-brown, while the stems of the ‘White’ variety are green, and the leaves are more coarsely serrated in the White. The oil furnished by the Black is of inferior quality, but more abundant than that obtained from the White, the yield of oil from which is generally only about four-fifths of that from an equal area of the Black, but it has a more delicate odor and obtains a higher price. The plant is also more delicate, being easily destroyed by frost or drought; it is principally grown for drying in bundles – technically termed ‘bunching,’ and is the kind chiefly dried for herbalists, the Black variety being more generally grown for the oil on account of its greater productivity and hardiness.
The Basics:
White Peppermint is a very important and commonly used remedy, being employed by allopathic doctors as well as herbalists. It is also widely used as a domestic remedy. A tea made from the leaves has traditionally been used in the treatment of fevers, headaches, digestive disorders (especially flatulence) and various minor ailments. An infusion is used in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, digestive problems, spastic colon etc. Externally a lotion is applied to the skin to relieve pain and reduce sensitivity.
The essential oil in the leaves is antiseptic and strongly antibacterial, though it is toxic in large doses. When diluted it can be used as an inhalant and chest rub for respiratory infections. The essential oil is used in aromatherapy. Its keyword is “Cooling”.
Peppermint is one of the best carminative agents available. It has a relaxing effect on the visceral muscles, anti-flatulent properties and stimulates bile and digestive juice secretion, and so can relieve intestinal colic, flatulent dyspepsia and other associated conditions.
The volatile oil acts as a mild anesthetic to the stomach wall, which helps to relieve the vomiting of pregnancy and travel sickness. Peppermint plays a role in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. It is most valuable in the treatment of fevers and especially colds and flu.
As an inhalant it can be used as a temporary treatment for nasal catarrh. Where migraine headaches are associated with the digestion, this herb may be used. As a nervine it eases anxiety and tension. In painful periods it relieves the pain and eases tension. Externally it relieves itching and inflammation.
Peppermint oil is useful in combating flatulence and mild indigestion. Many over-the-counter stomach aids contain Peppermint to both enhance the taste as well as the effectiveness of the medicine. However, in a strange bit of irony, Peppermint is something of a trigger food for many suffering from acid reflux and may cause their symptoms to worsen.
How does it work? Peppermint oil seems to reduce spasms in the digestive tract. When applied to the skin, it can cause surface warmth, which relieves pain beneath the skin.
Continue reading
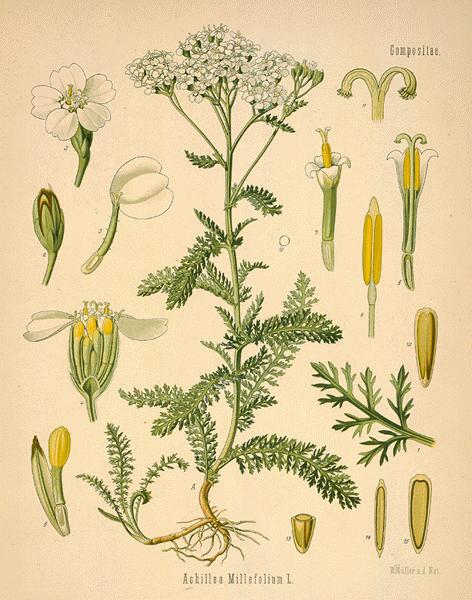
Yarrow
- Scientific Name: Achillea millefolium
- Plant Family: Compositae
- Parts Used: The whole plant – stems, leaves, flowers, collected in the wild state, in August, when in flower.
- Actions: Diaphoretic, Hypotensive, Astringent, Diuretic, Antiseptic, Anticatarrhal, Emmenagogue, Hepatic, Stimulant, Tonic, Mild Aromatic
The Basics:
Yarrow is a wound herb, astringent and healing, and rich in vitamins and minerals. Bind bruised fresh leaves to cuts, or make an ointment by pounding the flowers and mixing with coconut oil, or bathe wounds with yarrow tea. The tea is also a good tonic drink, it restores lost appetite and promotes perspiration during colds and fevers. Chew fresh leaves to soothe toothache.
Yarrow also lowers blood pressure due to a dilation of the peripheral vessels. It stimulates the digestion and tones the blood vessels. As a urinary antiseptic it is indicated in infections such as cystitis. It is considered to be a specific in thrombotic conditions associated with high blood pressure.
The flowers are often steamed and inhaled to treat hay fever and asthma and in teas for respiratory problems, as a wash for eczema and other skin conditions; and in chest rubs for cold, flu, and inflamed joints. Continue reading
Rennie Luttrull: queen-annes-lace-seeds
Rosanna: Spignel aka Bald Money
Annamarie Squatrito: Fumitory
EILEEN Klinghagen: Pumpkin
Mahmudul Hasan: Celery