Shrubby Medicinals
Juniper
- Scientific Name: Juniperus, communis
- Plant Family: Pinaceae
- Parts Used: Berries, leaves and twigs, bark
- Constituents: Rich in essential oil which contains monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes, invert sugar, flavone glyosides, resin, tannin, organic acids
- Actions: Diuretic, Stimulant, Carminative, Emmenagogue, Antimicrobial, Anti-rheumatic, Abortifacient
- How does it work? Juniper berries contain chemicals that might decrease swelling. It might also be effective in fighting bacteria and viruses. Juniper might also increase the need to urinate.
Varieties:
There are over sixty Juniper species, but the one which yields edible fruits in Britain is Juniperus comunis. In the Americas, Eastern Red Cedar, Juniperus virginiana, can be used in much the same way. A detailed account of the herbal properties of Eastern Red Cedar can be found here.
Among the varied forms, there are dense, columnar trees; medium sized, rounded shrubs; irregular bush forms; and creeping prostrate types. Irish and Swedish junipers are tall, narrow, and quick growing; the Greek and Chinese are very compact, slow growing. Pfitzers are irregular, massive types. California Juniper may reach heights of 40 feet, and shore Juniper and japonica are spreading ground covers.
Notes and Cautions:
One useful guide to the identification of Juniper is the apple-like fragrance that the needle-shaped leaves give off when crushed.
Women who are pregnant, wish to become pregnant, or who are nursing a child should not eat Juniper fruits. Due to their action on the kidneys, Juniper berries should be avoided by persons with kidney disease.
Don’t confuse Juniper berry oil with cade oil, which is distilled from Juniper wood (Juniperus oxycedrus).
The Basics:
A strong aromatic scent emanates from all parts of the shrub. Berries taste slightly bitter-sweet, fragrant, and spicy and are generally used to make a tea that is good for flatulence and indigestion, to promote the flow of urine.
Juniper branches can be used as a fumigant and were commonly burned in public places in times of plague and pestilence. This was still the practice in French hospitals a century ago during the smallpox epidemic of 1870.
Juniper berries make an excellent antiseptic in conditions such as cystitis. The essential oil present is quite stimulating to the kidney nephrons and so this herb should be avoided in kidney disease. The bitter action aids digestion and eases flatulent colic. It is used in rheumatism and arthritis. Externally it eases pain in the joints or muscles.
Some people take Juniper by mouth for problems with digestion, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and kidney and bladder stones along with many other conditions. Some people apply Juniper directly to the skin for wounds and pain in joints and muscles.
In foods, Juniper berry is often used as a condiment. The extract, oil, and berry are used as flavoring ingredients in foods and beverages. In manufacturing, Juniper extract and oil are used as fragrances in soaps and cosmetics.
Mastic Thyme aka Spanish Marjoram
- Scientific Name: Thymus mastichina
- Common Name: Spanish Marjoram
- Plant Family: Lamiaceae or Labiatae
- Parts Used: Leaves, Flowers, Essential Oil
- Actions: Antiseptic, Deodorant, Disinfectant, Analgesic, Anti-inflammatory, Antibacterial
General Overview
Thymus mastichina is a very special thyme, native in the mountains of the Iberian Peninsula, Central Spain and Portugal. It is known by a number of different common names including Spanish Marjoram, Spanish Wood Marjoram, White Thyme, Wild Marjoram or Mastic Thyme. The leaves, and especially the essential oil contained in them, are strongly antiseptic, deodorant and disinfectant.
Thymus mastichina should not be confused with Marjoram also known as sweet Marjoram, knotted Marjoram and previously classed as Marjorana hortensis (Origanum majorana). Nor should it be confused with the Mastic Tree (Pistacia lentiscus).
As the name implies it grows primarily in Spain. Thymus mastichina produces tiny, oval-shaped, green leaves, which have an intense flavor. In its Spanish homeland it is used as a culinary herb for meat dishes, stews and sauces and because of its strong aroma has been commonly used in Andalucía to season and preserve olives.
Despite this fact, it is prized more for its essential oils than for its herbal properties. The plant has an herbaceous scent with eucalyptus-like overtones with a hint of a vanilla note, which, in aromatherapy, is used for its soothing, relaxing effect. It’s oil is pale orange to amber in color and has a distinctive eucalyptus like aroma. It is also considered to be especially beneficial in relaxing muscles.
Used fresh or in dried form, its leaves are used to make an herbal tea that is considered useful in treating sore throats, catarrh and colds. If preferred, the tea can be used to gargle with rather than ingested. Infusions are attributed curative or palliative properties of arthritis and rheumatism. Mastic Thyme, may be effective in protecting against colon cancer.
The Basics
The species name mastichina and the common name of Mastic Thyme derive from the Greek word massein, meaning ‘to chew’, or the verb mastichein meaning ‘to gnash the teeth’. It is the origin of the English word masticate.
Interestingly, the Mastic Tree is a small Mediterranean evergreen tree (Pistacia lentiscus) of the cashew family. The tree produces an aromatic, ivory-coloured resin, also known as mastic, is harvested as a spice from the cultivated mastic trees grown in the south of the Greek island of Chios in the Aegean Sea. Mastic resin is a relatively expensive kind of spice that has been used principally as a chewing gum. The flavor can be described as a strong, slightly smoky, resiny aroma.
Mastic Thyme produces tiny, oval-shaped, green leaves, which have an intense flavor. In its Spanish homeland it is used as a culinary herb for meat dishes, stews and sauces and because of its strong aroma has been commonly used in Andalucía to season and preserve olives.
Despite this fact, it is prized more for its essential oils than for its herbal properties. The plant has an herbaceous scent with eucalyptus-like overtones with a hint of a vanilla note, which, in aromatherapy, is used for its soothing, relaxing effect. It is also considered to be especially beneficial in relaxing muscles. The essential oil is most often found under the name: Spanish Marjoram.
Used fresh or in dried form, its leaves are used to make an herbal tea that is considered useful in treating sore throats, catarrh and colds. If preferred, the tea can be used to gargle with rather than ingested. Infusions are attributed curative or palliative properties of arthritis and rheumatism.
The leaves are used as a seasoning. They have a pungent eucalyptus-like aroma. If the leaves are to be dried, the plants should be harvested in early and late summer just before the flowers open and the leaves should be dried quickly. The plant is also the source of an essential oil, called “oil of marjoram” or “Spanish Marjoram”, that is used extensively as a flavoring for soups etc.
The essential oil obtained from the leaves is also used in perfumery, as a mouth wash, medicinally etc.
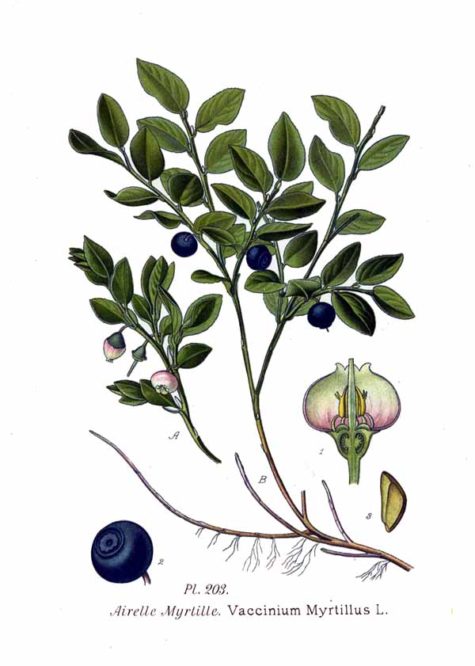
Bilberry
- Scientific Name: Vaccinium myrtillus
- Plant Family: N.O. Vacciniaceae
- Parts Used: The ripe fruit. The leaves.
- Actions: astringent, diuretic, tonic, antiseptic,antibacterial
Varieties:
- V. arboreum, or Farkleberry. This is the most astringent variety, and both berries and root-bark may be used internally for diarrhoea, chronic dysentery, etc. The infusion is valuable as a local application in sore throat, chronic ophthalmia, leucorrhoea, etc.
- V. resinosum, V. damusum, and V. gorymbosum have properties resembling those of V. myrtillus.
- The Bog Bilberry ( V. uliginosum) is a smaller, less erect plant, with round stems and untoothed leaves, greyish green beneath. Both flowers and berries are smaller than those of the common Bilberry. This kind is quite absent in the south and only to be found in mountain bogs and moist copses, in Scotland, Durham and Westmorland.
- The ‘Huckleberry’ of North America, so widely appreciated there, is our Bilberry – the name being an obvious corruption of ‘Whortleberry.’
Constituents: The leaves contain glucoquinones, which reduce the levels of sugar in the blood. The skin of the fruits contains anthocyanin and is specific in the treatment of hemeralopia (day-blindness). The fruit is a rich source of anthocyanosides, which have been shown experimentally to dilate the blood vessels.
The Basics:
Although often called huckleberry, the bilberry is more nearly related to the cranberry. Vaccinium myrtillus has been used for nearly 1,000 years in traditional European medicine. Bilberry fruits have been used in the traditional Austrian medicine internally (directly or as tea or liqueur) for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and diabetes. Herbal supplements of V. myrtillus (bilberry) on the market are used for circulatory problems, as vision aids, and to treat diarrhea and other conditions.
Bilberry is a well-known folk remedy for poor vision, especially for people who suffer from “night blindness,” that is, they have difficulty seeing in the dark. In fact, bilberry jam was given to Royal Air Force pilots who flew nighttime missions during World War II. It works by accelerating the regeneration of retinol purple, commonly known as visual purple, a substance that is required for good eyesight. European medical journals are filled with studies confirming bilberry’s positive effect on vision. Unfortunately, this herb has not received the attention it deserves in the American medical community so far.
Some people use bilberry for conditions of the heart and blood vessels including hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), varicose veins, decreased blood flow in the veins, and chest pain. Bilberry is also used for chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), hemorrhoids, diabetes, osteoarthritis, gout, skin infections, gastrointestinal (GI) disorders, kidney disease, and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
The dried leaves of bilberries are used in the treatment of a variety of complaints. A tea made from the dried leaves is strongly astringent, diuretic, tonic and an antiseptic for the urinary tract. It is also a remedy for diabetes if taken for a prolonged period. Another report says that the leaves can be helpful in pre-diabetic states but that they are not an alternative to conventional treatment. The leaves contain glucoquinones, which reduce the levels of sugar in the blood.
A decoction of the leaves or bark is applied locally in the treatment of ulcers and in ulceration of the mouth and throat. It is sometimes applied directly to the inside of the mouth for mild mouth and throat soreness. A distilled water made from the leaves is an excellent eyewash for soothing inflamed or sore eyes.
Whilst the fresh fruit has a slightly laxative effect upon the body, when dried it is astringent and is commonly used in the treatment of diarrhea etc. The dried fruit is also antibacterial and a decoction is useful for treating diarrhea in children. The skin of the fruits contains anthocyanin and is specific in the treatment of hemeralopia (day-blindness). The fruit is a rich source of anthocyanosides, which have been shown experimentally to dilate the blood vessels, this makes it a potentially valuable treatment for varicose veins, hemorrhoids and capillary fragility.
How does it work?
Bilberry contains chemicals called tannins that can help improve diarrhea, as well as mouth and throat irritation, by reducing swelling (inflammation). There is some evidence that the chemicals found in bilberry leaves can help lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Some researchers think that chemicals called flavonoids in bilberry leaf might also improve circulation in people with diabetes. Circulation problems can harm the retina of the eye. Continue reading
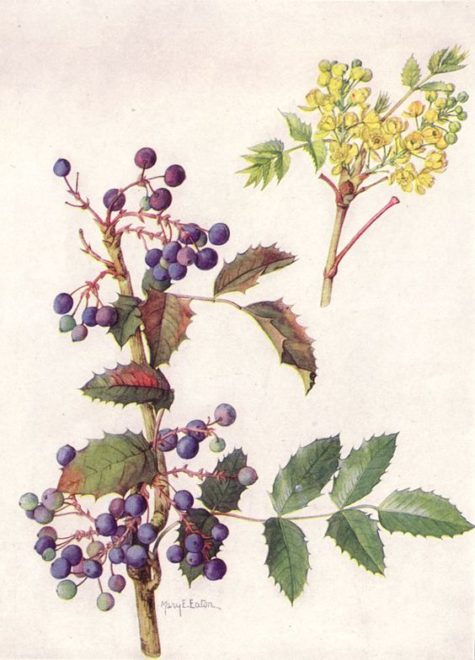
Oregon Grape
- Scientific Name: Berberis Aquifolium
- Common Name: Barberry
- Plant Family: Berberidaceae
- Parts Used: Rhizome and Roots, Bark, Fruits
- Actions: Alterative, cholagogue, diuretic, laxative and tonic
Description:
Several varieties of the subgenus Mahonia contribute to the drug of commerce under the name of Berberis aquifolium. It is a quickly-growing shrub about 6 feet high: the oddly compound leaves have no spine at the base; they are evergreen and shining. The flowers grow in terminal racemes, are small and yellowish-green in color, and the purple berries are three- to nine-seeded. The bark is brown on the surface and yellow beneath. The root is from 1/2 inch in diameter to 3 inches at the base of the stem, odorless, and with a bitter taste. The shrub was introduced into England from North America in 1823. It was formerly known as Mahonia aquifolia and is very hardy.
Note:It should not be used with Glycyrrhiza species (Liquorice) because this nullifies the effects of the berberine.
The Basics:
Oregon grape was often used by several native North American Indian tribes to treat loss of appetite and debility. Its current herbal use is mainly in the treatment of gastritis and general digestive weakness, to stimulate the kidney and gallbladder function and to reduce catarrhal problems. The root and root bark is alterative, blood tonic, cholagogue, diuretic, laxative and tonic. It improves the digestion and absorption and is taken internally in the treatment of psoriasis, syphilis, haemorrhages, stomach complaints and impure blood conditions. Externally, it has been used as a gargle for sore throats and as a wash for blurry or bloodshot eyes.
The blue fruits are tart and improve after frost. They are often gathered for jelly or wine. Used to treat a wide variety of ailments, Oregon Grape species contain the extremely potent alkaloid, berberine, (also found in goldenseal) which is antiseptic and stimulates the liver and spleen.
The fruit is an excellent gentle and safe laxative. Berberine, universally present in rhizomes of Mahonia species, has marked antibacterial effects and is used as a bitter tonic. Since it is not appreciably absorbed by the body, it is used orally in the treatment of various enteric infections, especially bacterial dysentery.
Berberine has also shown anti-tumor activity.
It is one of the best alterative blood purifiers and liver stimulants. Uses for the Oregon Grape Root include weak digestion, flatulence, jaundice, blood impurities, and as a general tonic to the whole system.
A decoction (instructions below) will be found to be a wonderful blood purifier and will restore health to many who are suffering from a sluggish liver, weak stomach, indigestion, and sallow skin.
Years ago, it was given to children, and said to create appetite and promote digestion, and increase strength and vitality. The current medical thinking is that it is not safe for children, especially infants, or pregnant or nursing women. (see information at the bottom of the post)
Continue reading
Rennie Luttrull: queen-annes-lace-seeds
Rosanna: Spignel aka Bald Money
Annamarie Squatrito: Fumitory
EILEEN Klinghagen: Pumpkin
Mahmudul Hasan: Celery