Justice
Winged Balancer of Life,
Dark-faced Goddess, Daughter of Justice
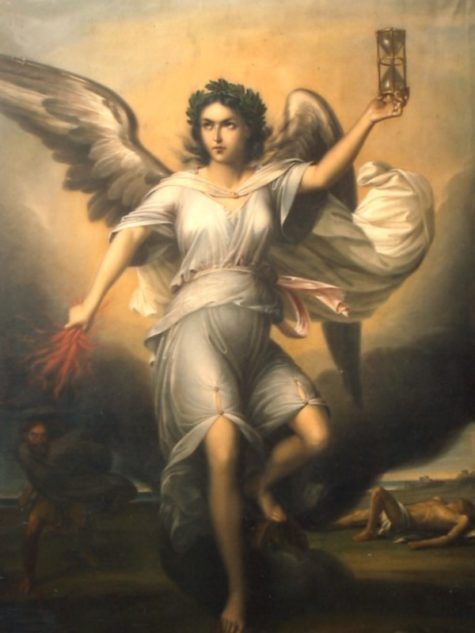
Nemesis is the Greek Goddess of balance, justice, retribution, and vengeance. Evil deeds, undeserved good fortune, and crimes that go unpunished or that bring rewards, may invoke Her wrath and remorseless justice and retribution.
Nemesis resembles modern images of angels. She is a winged, wreathed woman, usually dressed in white. She can also be seen as a Griffon holding a Wheel of Fortune. She is sometimes known as, Adrasteia, which means “The Inescapable.”
- Other Names: Rhamnousia, Rhamnusia, Adrasteia, Adrestia
- Plant: Mullein
- Creature: Griffin, Goose
- Festival: The Nemesia
- Symbols: The wheel, wings, whip or sword, dagger, measuring rod, hourglass, bridle, scales, branch laden with apples
Nemesis measures out happiness and unhappiness making sure that happiness does not occur excessively. If you are arrogant before the Gods, she will mete out the punishment. What goes around comes around and you can be sure that Nemesis will use Her powers against those who deserve it.
She is implacable and remorseless, but she is not cruel. Nemesis distributes just deserts. She is the spirit of righteous, justified anger, directing her powers against those who have violated cosmic order. Nemesis has broader jurisdiction than the Erinyes, who may be her sisters. While the Erinyes only avenge shed blood, Nemesis takes action wherever natural laws are flouted, broken, or disrespected.
Nemesis serves as a personal goddess offering protection and sponsorship to devotees. Those who invoke her protection are expected to behave honorably and to uphold natural moral code. You can find spells and rituals that invoke Nemesis in the Book of Shadows.
It is believed that Nemesis is the daughter of Nyx the dark Goddess of night and Erebus, God of the Underworld. Her closest companion is Aidos, the Goddess of Shame. Greek prophesies suggests that when humans become more wicked than good, Nemesis and Aidos will abandon the Earth and then all hell will break loose!
Nemesis hasn’t left yet and is still administering justice. German painter Alfred Rethel painted her as an avenging angel in hot pursuit in his 1837 painting, “Nemesis Pursuing a Murderer.” According to legend, a high-ranking man with secret, undiscovered crimes on his conscience won Rethel’s painting in a Frankfurt lottery. Contemplation of Nemesis’ portrait allegedly drove him mad.
Nemesis Stones
Nemesis Stones are stones taken from an altar of Nemesis. Stones are engraved with an image of Nemesis, usually in the form of a young woman standing with one foot on a wheel. They are worn as amulets around the neck and set into rings. They exorcise and ward off evil spirits as well as preventing and banishing nightmares and healing the moonstruck.
Spirit Allies:
Nemesis’ closest companion is Aidos, Goddess of Shame, and Artemis is Nemesis’ good friend. She may be worshiped together with Themis, Goddess of Divine Order. Nemesis is often found in the company of Tyche, Goddess of Fortune, if only to ensure that people get what they deserve.
Origins:
As the “Goddess of Rhamnous”, Nemesis was honored and placated in an archaic sanctuary in the isolated district of Rhamnous, in northeastern Attica. There she was a daughter of Oceanus, the primeval river-ocean that encircles the world.
Pausanias noted her iconic statue there. It included a crown of stags and little Nikes and was made by Pheidias after the Battle of Marathon (490 BC), crafted from a block of Parian marble brought by the overconfident Persians, who had intended to make a memorial stele after their expected victory. Her cult may have originated at Smyrna.
Nemesis and Helen of Troy
In some metaphysical mythology, Nemesis produced the egg from which hatched two sets of twins: Helen of Troy and Clytemnestra, and the Dioscuri, Castor and Pollux. While many myths indicate Zeus and Leda to be the parents of Helen of Troy, the author of the compilation of myth called Bibliotheke notes the possibility of Nemesis being the mother of Helen.
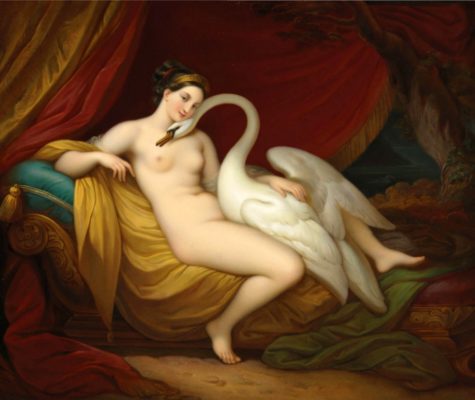
Nemesis, to avoid Zeus, turns into a goose, but he turns into a swan and mates with her. The story is as follows:
Rich-haired Nemesis gave birth to Helene when she had been joined in love with Zeus the king of the gods by harsh violence. For Nemesis tried to escape him and liked not to lie in love with her father Zeus the son of Kronos; for shame and indignation vexed her heart: therefore she fled him over the land and fruitless dark sea.
But Zeus ever pursued and longed in his heart to catch her. Now she took the form of a fish and sped over the waves of the loud-roaring sea, and now over Oceanus’ stream and the furthest bounds of Earth, and now she sped over the furrowed land, always turning into such dread creatures as the dry land nurtures, that she might escape him.
Nemesis, as she fled from Zeus’ embrace, took the form of a goose; whereupon Zeus as a swan had intercourse with her. From this union she laid an egg, which some herdsman found among the trees and handed over to Leda. She kept it in a box, and when Helene was hatched after the proper length of time, she reared her as her own. It is in this way that Leda comes to be the mother of Helen of Troy.
Here is a slightly different story, which also explains the creation of the Constellation Cygnus (or the Swan):
When Zeus, moved by desire, had begun to love Nemesis, and couldn’t persuade her to lie with him, he relieved his passion by the following plan. He bade Venus Aphrodite, in the form of an eagle, pursue him; he, changed to a swan, as if in flight from the eagle, took refuge with Nemesis and lighted in her lap. Nemesis did not thrust him away, but holding him in her arms, fell into a deep sleep.
While she slept, Zeus embraced her, and then flew away. Because he was seen by men flying high in the sky, they said he was put in the stars. To make this really true, Jupiter put the swan flying and the eagle pursuing in the sky. But Nemesis, as if wedded to the tribe of birds, when her months were ended, bore an egg. Hermes took it away and carried it to Sparta and threw it in Leda’s lap. From it sprang Helen, who excelled all other girls in beauty.
Nemesis and Narcissus
Although a respected goddess, Nemesis brought much sorrow to mortals such as Echo and Narcissus. Narcissus was a very beautiful and arrogant hunter from the territory of Thespiae and Boeotia, who disdained the ones who loved him.
Nemesis lured him to a pool where he saw his own reflection in the water and fell in love with it, not realizing it was only an image. He was unable to leave the beauty of his reflection and he eventually died. Nemesis believed that no one should ever have too much goodness in their lives, and she had always cursed those who were blessed with countless gifts.
Sources:
- Wikipedia
- Encyclopedia of Spirits
Also known as The Ten Kings, or the Ten Judges of Hell; the Ten Kings of Hell are afterlife judges. They derive from Chinese Taoist tradition, filtered through Japanese Buddhism.
- Those who have clearly lived exemplary lives travel to Paradise.
- Those who have been clearly wicked travel to a punishment realm.
But what of those whose actions are more ambiguous? Those who may have performed both good and bad deeds while alive? Where do they go? That’s for the Kings of Hell to decide.
The Kings of Hell preside over a series of afterlife trials intended to determine the fate of the dead soul. The person’s actions while alive, both positive and negative are weighed, analyzed and discussed. Jizo serves as the defense attorney for dead souls and always attempts to present human actions in the best possible light. Final outcome, however is up to the Kings of Hell.
The Eighteen Levels of Hell
Chinese legends speak of the “Eighteen Levels of Hell”. Each court deals with a different aspect of atonement and different punishments; most legends claim that sinners are subjected to gruesome tortures until their “deaths”, after which they are restored to their original state for the torture to be repeated.
The concept of the eighteen hells started in the Tang dynasty. The Buddhist text Wen Diyu Jing mentioned 134 worlds of hell, but was simplified to the Eighteen Levels of Hell for convenience. Sinners feel pain and agony just like living humans when they are subjected to the tortures listed below. They cannot “die” from the torture because when the ordeal is over, their bodies will be restored to their original states for the torture to be repeated. The following is a list of common punishments and tortures in the hells:
- Mountain of Knives: Sinners are thrown off cliffs and land on mountainous terrain with sharp blades sticking out. Some depictions show offenders climbing trees with knives or sharp thorns sticking out of trunks and branches.
- Cauldron torture: Sinners are fried in cauldrons of oil.
- Dismemberment: Sinners are dismembered by various means, including sawing, slicing into half, mashing/pounding into pulp, being crushed by rocks/boulders, being run over by vehicles, etc.
- Grinding torture: Sinners are put into a grinding machine and ground into a bloody pulp.
- Burning: Sinners are set aflame or cast into infernos.
- Paolao torture: Sinners are stripped naked and tied to a large hollow metal cylinder with a fire lit at its base.
- Boiling liquid torture: Boiling liquids are forced down sinners’ throats or poured on parts of their bodies.
- Tortures involving removal of body parts or organs: Tongue ripping, eye gouging, teeth extraction, heart digging, disembowelment, skinning, etc.
- Ice World: Sinners are frozen in ice. Some depictions show unclothed sinners suffering frostbite in an icy world. Their bodies eventually fall apart or break into pieces.
- Scales and hooks torture: Sinners are pierced with hooks and hung upside-down. Some depictions show sinners having nails hammered into their bodies.
- Pool of Blood: Sinners are cast into a pool of filthy blood, where they drown. Blood spills from all bodily orifices.
- Tortures involving animals: Sinners are trampled by cattle, gored by animals with horns or tusks, mauled or eaten by predators, stung or bitten by poisonous species, etc.
- Avīci: The period of suffering in this chamber is the longest. It is reserved for sinners who have committed heinous crimes, including the Five Grave Offences.
Some literature refers to eighteen types of hells or to eighteen hells for each type of punishment. Some religious or literature books say that wrongdoers who were not punished when they were alive are punished in the hells after death.
The Five Grave Offences:
Ānantarika-karma or ānantarika-kamma is a heinous crime that through karmic process brings immediate disaster. They are called ‘anantarika’ because they are ‘an’ (without) ‘antara’ (interval), in other words the results immediately come to fruition in the next life, i.e. the participant goes straight to hell.
These are considered so heinous that Buddhists and non-Buddhists must avoid them. According to Buddhism, committing such a crime would prevent the perpetrator from attaining the stages of sotāpanna, sakadagami, anāgāmi or arhat in that lifetime. The five crimes are:
- Intentionally murdering one’s father.
- Intentionally murdering one’s mother.
- Killing an Arhat (fully enlightened being).
- Shedding the blood of a Buddha.
- Creating a schism within the Sangha, the community of Buddhist monks, nuns and pariṣā who try to attain enlightenment.
In Mahayana Buddhism these five crimes are referred to as pañcānantarya and are mentioned in “The Sutra Preached by the Buddha on the Total Extinction of the Dharma”.
Source: Wikipedia
Ra (pronounced as Rah, and sometimes as Ray) is an ancient Egyptian sun god. By the fifth dynasty he became a major deity in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the mid-day sun, with other deities representing other positions of the sun. Ra changed greatly over time and in one form or another, much later he was said to represent the sun at all times of the day.
Also known as:
- Re
- Phra
- Amun-Ra
- Akmun-Ra
Ra should be pronounced as ‘rei’; hence the alternative spelling Re rather than Ra. The meaning of Ra’s name is uncertain, but it is thought if not a word for ‘sun’ it may be a variant of or linked to ‘creative’. As his cult arose in the Egyptian pantheon, Ra often replaced Atum as the father, grandfather, and great-grandfather of the deities of the Ennead, and became a creator of the world.
Ra was an incredibly powerful and important central god of the Egyptian pantheon. His believers considered him to be the god who created everything. He was worshiped more than any other god by the ancient Egyptians.
Ra represents sunlight, warmth and growth. It was only natural that the ancient Egyptians would believe him to be the creator of the world, as well as part of him being represented in every other god. The ancient Egyptians believed that every god should illustrate some aspect of him, while Ra himself should also represent every god.
Ra created himself from the primordial chaos. He is also known as Re and Atum. His children are Shu, the God of Dry Air and Father of the Sky, and his twin sister Tefnut, the Goddess of Moisture and Wetness. Humans were created from Ra’s tears.
Invoked For:
He is the source of all light and life, destroyer of darkness, night, wickedness, evil. Creator of Heaven, Earth, and the Underworld. Eternal god without end. God of all agriculture, the Sun, magick, prosperity, spells, rituals, destiny, right, and truth.
Sun Ra Invocation:
As the sun pierces your consciousness and you struggle through those dog days of summer, it becomes easy to understand the ancient Egyptian respect for the Sun God. Pay tribute to Ra for his blessings in the way he likes best. In ancient Egypt, myrrh was burned at high noon to please him.
Put a few small chunks of myrrh on a white charcoal block placed on a fireproof surface outdoors. Use your hands to gently brush the smoke upward toward the heavens as you chant:
In honor and praise I send this smoke toward you
Thanks for the blessings and the sunny days, too
Sun Ra, great god, emblem of the sun
I honor and praise you for all that you’ve done.
Titles and Epithets:
- The Creator
- The Supreme Power
- The Only One
- Great Father
- Father of the Gods
- Sun God.
- Lord of the Circles
The ancient Egyptians revered Ra as the god who created everything. Also known as the Sun God, Ra was a powerful deity and a central god of the Egyptian pantheon. The ancient Egyptians worshiped Ra more than any other god and pharaohs often connected themselves with Ra in their efforts to be seen as the earthly embodiment of the Sun God.
Ra is the head of the Great Ennead (the nine deities of Atum, Geb, Isis, Nut, Osiris, Nephthys, Seth, Shu, and Tefnut), supreme judge; often linked with other gods aspiring to universality, and king of the gods until Osiris took over his throne. Ra was often lauded as “Lord of the Circles” and as “he who entereth (or liveth) in the circle.” He was described as “the sender forth of light into his circle” and as the “Governor of (his) circle.”
Symbolism
For the Egyptians, the sun represented light, warmth, and growth. This made sun deities very important to Egyptians, and it is no coincidence that the sun came to be the ruler of all. In his myths, the sun was either seen as the body or Eye of Ra.
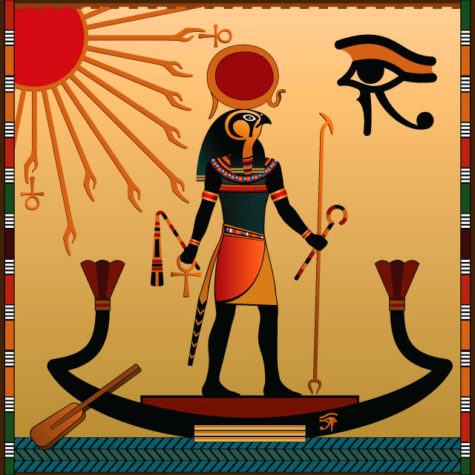
In artwork Ra primarily is depicted as a man wearing a pharaoh’s crown (a sign of his leadership of the deities) and the sun disk, or Wadjet sun disk above his head.
- The Sun Disk
The sun disk that surrounded his head symbolizes what the god represents, including sunlight, warmth and growth. As he was the god of creation, the sun disk represents the light and energy needed for life.
The Wadjet sun disk, is a sun disk with a cobra wrapped around it. Called the Wadjet sun disk because the goddess Wadjet, was depicted as an Egyptian cobra, an animal thought only to be female and reproducing through parthenogenesis. It is also shown as the hieroglyphic Ankh, symbolizing the life given by the sun.
Some traditions relate that the first Wadjet was created by the goddess Isis who formed it from the dust of the earth and the spittle of Atum. The uraeus was the instrument with which Isis gained the throne of Egypt for her husband Osiris. As the sun, Ra was thought to see everything.
- Eye of Ra
Present in the ancient Egyptian mythology is the Eye of Ra, shown as the sun disk with two ‘uraeus’ cobras coiled around it, next to the white and red crowns of Upper and Lower Egypt. Initially associated with Horus (similarly to the Wadjet, the Eye of Horus), the Eye of Ra shifted positions in the myths, becoming both an extension of Ra’s power and a separate entity altogether.
- The Falcon
He was associated with the falcon, the symbol of other sun deities who protected the pharaohs in later myths.

Ra shared many of his symbols with other solar deities, in particular Horus, usually depicted as a falcon. After the deities were paired with pharaohs, the children of Hathor were considered to be fathered by Ra.
- The Tree of Life
The Tree of Life is an important religious symbol to the Egyptians. The Tree of Life was located within Ra’s sun temple in Heliopolis and was considered sacred. The fruit that sprang from this tree was not available to humans, but only in aging-rituals reserved for pharaohs. The Tree of Life is also referred to as the mythical, sacred Ished tree. Eternal life came to those who ate the fruit from the Tree of Life.
- Bennu Bird or Phoenix
Another important ancient Egyptian symbol connected to Ra is the “Bennu.” The Bennu bird is Ra’s ba and a symbol of fire and rebirth. Bennu is the name of the bird that represented Ra’s soul.
This bird is a phoenix and it was seated at the Tree of Life in Ra’s Sun Temple in Heliopolis. Inside the temple, on top of an obelisk, sat the Benben Stone. This pyramid-shaped stone served as a beacon to Bennu and is also an important ancient Egyptian religious symbol. Sometimes, Ra is depicted as a phoenix, showing the connection between the two.
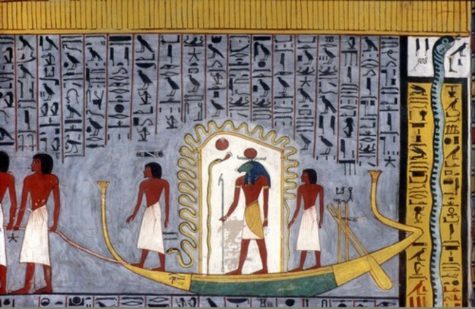
- Primordial Serpent and Sun Boat
Ra was thought to travel in a sun boat to protect its fires from the primordial waters of the underworld it passed through during the night.
The ancient Egyptians believed that as the sun god, Ra’s role was to sail across the heavens during the day in his boat called the “Barque of Millions of Years.” In the morning when Ra emerged from the east, his boat was named, “Madjet” which meant “becoming strong.” By the end of the day the boat was called, “Semektet” which meant “becoming weak.” At the end of the day, it was believed that Ra died (swallowed by Nut) and sailed on to the underworld, leaving the moon in his place to light up the world.
The ancient texts describe how Ra would go down with the setting sun into the underworld and then rise again the next day on the opposite side. This also symbolizes the same journey that the deceased would take right after burial.
The journey was divided into 12 hours, with each hour representing an obstacle that Ra had to complete in order to move onto the next. Each area has gods and monsters that Ra meets along the way.
Throughout his journeys and adventures, the serpent-god Apep is his greatest enemy. Apep would hide below the horizon waiting to attack Ra, and they would fight many battles. Many gods and goddesses were involved in defending Ra, including the god Seth.
Ra was reborn at dawn the very next day. Ra traveled in the sun boat with various other deities including Set and Mehen who defended against the monsters of the underworld, and Ma’at who guided the boat’s course. The monsters included Apep, an enormous serpent, or also, The Lord of Chaos, who tried to stop the sun boat’s journey every night by consuming it. In some stories, Ra, in the form of a cat named Mau, defeats the evil serpent, Apep. This is part of the reason why cats are so highly-revered in Egypt.
The Ra myth saw the sunrise as the rebirth of the sun by the goddess Nut and the sky, thus attributing the concept of rebirth and renewal to Ra and strengthening his role as a creator god.
In the Pyramid Text, Re is perpetually resurrected in the mornings in the form of a scarab beetle, Khepri, which means the Emerging One. He rides on the primordial waters, called Nun, in his sacred bark (boat) along with a number of other deities across the sky. At noon he is the falcon-headed man Harakhty, and at sunset the elder Atum, the “All Lord.” He is then swallowed by the goddess Nut, who gives birth to him each morning again as Khepri.
Therefore, the cycle continued with birth, life and death. This constant aging was suggested by some later Egyptians as the reason Ra stayed separate from the world and let Osiris or Horus rule in his place.
Often coupled with this idea is the myth in which Isis is able to trick an elderly Ra, having ruled on earth as a human pharaoh, into revealing his secret name, and thus the secret of his power. Ra subsequently lost his power, resulting in the cult of Isis and Osiris to rise in importance.
- Other Symbols
The Obelisk represents the rays of the sun and was worshiped as a home of a solar god. Other symbols include Pyramids aligned east to west, the Bull, Serpent, Heron, Lion, Cat, Ram, Hawk, Beetle, and others. His main symbol, however, is the sun disk.
Ra’s Appearance
Ra is usually shown in his human form with a falcon head crowned with a sun disc. The famous sun disc was surrounded by a sacred cobra named Uraeus. In some artistic representations of the god, he is shown as “a man with the head of a beetle” or sometimes as “a man with the head of a ram”.
Sometimes Ra is shown in animal form; most commonly, Ra is shown as a hawk, but sometimes also a beetle, lion, ram, or snake, as all of these were considered powerful animals in ancient Egypt. In iconography, Egyptians sometimes painted Ra as simply a large solar disk between two large falcon wings. Ra was incorporated into many aspects of Egyptian art, and he can be seen in paintings, sculptures, statues, and even jewelry.
Composites
As with most widely worshiped Egyptian deities, Ra’s identity was often confused with others as different regional religions were merged in an attempt to unite the country.
- Amun Re
Amun was a member of the Ogdoad, representing creation energies with Amaunet, a very early patron of Thebes. He was believed to create via breath, and thus was identified with the wind rather than the sun. As the cults of Amun and Ra became increasingly popular in Upper and Lower Egypt respectively they were combined to create Amun-Ra, a solar creator god. The name Amun-Ra is reconstructed).
It is hard to distinguish exactly when this combination happened, but references to Amun-Ra appeared in pyramid texts as early as the fifth dynasty. The most common belief is that Amun-Ra was invented as a new state deity by the (Theban) rulers of the New Kingdom to unite worshipers of Amun with the older cult of Ra around the eighteenth dynasty.
- Atum-Ra
Atum-Ra (or Ra-Atum) was another composite deity formed from two completely separate deities, however Ra shared more similarities with Atum than with Amun. Atum was more closely linked with the sun, and was also a creator god of the Ennead. Both Ra and Atum were regarded as the father of the deities and pharaohs, and were widely worshiped. In older myths, Atum was the creator of Tefnut and Shu, and he was born from ocean Nun.
- Ra-Horakhty
In later Egyptian mythology, Ra-Horakhty was more of a title or manifestation than a composite deity. It translates as “Ra (who is) Horus of the Horizons”. It was intended to link Horakhty (as a sunrise-oriented aspect of Horus) to Ra. It has been suggested that Ra-Horakhty simply refers to the sun’s journey from horizon to horizon as Ra, or that it means to show Ra as a symbolic deity of hope and rebirth.
- Khepri and Khnum
Khepri was a scarab beetle who rolled up the sun in the mornings, and was sometimes seen as the morning manifestation of Ra. Similarly, the ram-headed god Khnum was also seen as the evening manifestation of Ra. The idea of different deities (or different aspects of Ra) ruling over different times of the day was fairly common, but variable.
With Khepri and Khnum taking precedence over sunrise and sunset, Ra often was the representation of midday when the sun reached its peak at noon. Sometimes different aspects of Horus were used instead of Ra’s aspects. In Thelema’s Liber Resh vel Helios, Ra represents the rising sun, with Hathor as the midday sun and Tum as the setting sun.
- Ptah
Ra rarely was combined with Ptah; the sun “crosses” over Ptah in the underworld before Ptah is reborn, thus there would be no sun-ray when this happens. Other combinations can and do exist: The rising sun with sun ray, the noon sun with sun ray, and sitting sun with sunray. But as per the Memphite creation myth he was often said to be Ptah’s first creation, through his divine will, especially when associated with Atum or Amun.
The Legend of Ra Isis and The Snake
Although Ra was highly revered and devoutly worshiped by the ancient Egyptians, there is a story to suggest he eventually grew weak. In the Legend of Ra, Isis and the Snake, the goddess Isis knew that Ra had a secret name. This secret name possessed immense power and would allow her to perform magic spells whenever she desired to.
She knew that Ra wouldn’t willingly tell her the name so she quickly got to work. Ra had begun to age and sometimes saliva dribbled from his mouth. Isis visited with him one day. She collected the spit that dribbled down his chin and mixed it with dirt and clay. She shaped her mixture into a poisonous snake.
She set the snake in Ra’s path, and when Ra was out for a walk, the snake bit him and he immediately felt the poison rushing through his body. He was in tremendous pain and asked the other gods to help him. Isis promised to help Ra but only if he would tell her his secret name. He was resistant at first, but eventually, because of the pain he was in, Ra allowed Isis to “search through him” and in so doing, she healed him and Ra’s power was transferred over to her.
The Birth of Humans
One myth tells us that Ra first came to power during the golden age. Everything was perfect and just as it should be. The earth had not been tainted in any way. The sight of such perfection moved Ra to tears and they fell to the earth. The tears grew into humans.
At first, Ra was infatuated with watching humans interact and grow. But then he became angered with them as they ended the golden age that he had loved so much. They were cruel to each other and were ruining the earth.
He summoned the goddess Hathor and transformed her into a savage lioness. He then sent her to earth to kill every human. Hathor attacked every human she came across, killing most. But before she could eliminate all humans, Ra had a change of heart. He decided he needed to stop Hathor and did so by giving her enough beer to intoxicate her. She forgot her mission but the damage she had caused was permanent. Humans had been introduced to death and now all faced their immortality.
Quick Facts About Ra
- The ancient Egyptians worshiped Ra to such an extent above other gods that some historians have argued that ancient Egyptian religion was indeed a monotheistic one with Ra as the singular god.
- Historians believe that the pyramids might represent rays of sunlight, further connecting the pharaohs with Ra, the sun god.
- During Ra’s journey through the heavens he was accompanied by several other gods including Thoth, Horus, Hathor, Maat, Abtu, and Anet.
- Nut, goddess of the sky and heavens, is sometimes referred to as Ra’s mother, because he emerges from her and is reborn every morning.
- The morning manifestation of Ra is known as “Khepri the scarab God.”
- The evening manifestation of Ra is known as the ram-headed god, Khnum.
- The sacred cobra that encircled Ra’s crown symbolized royalty, sovereignty and divine authority.
- The right eye of Ra represented the Sun; while the left eye of Ra represented the moon.
- Ra is also closely associated with the Tree of Life myth, the Ben-Ben Stone and the Bennu Bird myths.
- Ra’s glory came to an end during the time when the Roman’s conquered Egypt in 30BC.
The Creation of Ra
Ra did not have parents. He is considered to be self-created and there are many myths that suggest how this came to be. It is said that before there was any land or recognizable landscapes, there was a body of water called Nun. The water was powerful and a shining egg arose from the darkness. Inside this egg was Ra. Sun rays landed on his body and gave him the power of sunlight. He then created all other elements of life by speaking their secret names. He spent his days traveling across the sky on a boat, where he carried prayers and blessings for the living.
At night, he would travel to the Underworld where Set and Mehen would help him defeat demons and monsters. He would leave the moon in the sky while traveling to the Underworld so that the living would still have light. It is said that he was reborn each day as the sun would rise over the horizon.
The Family of Ra
Ra had several siblings, including Apep, Thoth, Sobek and Serket.
Early in his myths Ra was said to be married to Hathor and they were the parents of Horus. Later his myths changed Hathor into Ra’s daughter. This featured prominently in the myth often called The Story of Sekhmet, in which Ra sent Hathor down to punish humanity as Sekhmet.
The Middle Kingdom saw Ra being increasingly combined and affiliated with other deities, especially Amun and Osiris.
Together with Atum, Ra was believed to have fathered Shu and Tefnut who in turn bore Geb and Nut. These in turn were the parents of Osiris, Isis, Set (also known as Seth), and Nephthys. All nine made up the Heliopolitan Ennead.
Worship of the Sun God
The New Kingdom brought new heights of worship to Ra. Many tombs in the Valley of the Kings portray depictions of Ra and his journey through the underworld. During this time, many solar temples were built.
Solar temples were built for Ra but did not contain a statue of the god. Instead, they were created to be open to the sunlight that Ra represented. The earliest known temple built in honor of Ra exists in Heliopolis meaning “City of the Sun” (now a Cairo suburb). This solar temple is known as “Benu-Phoenix” and is believed to have been erected in the exact spot where Ra emerged into creation.
In later Egyptian dynastic times, Ra was merged with the god Horus, as Re-Horakhty (and many variant spellings). When his worship reached this position of importance in the Egyptian pantheon, he was believed to command the sky, the earth, and the underworld.
His local cult began to grow from roughly the second dynasty, establishing Ra as a sun deity. By the fourth dynasty the pharaohs were seen to be Ra’s manifestations on earth. Fifth Dynasty and subsequent pharaohs were all known as “The son of Ra” and Ra became incorporated into every pharaoh’s name from then onward. His worship increased massively in the fifth dynasty, when he became a state deity and pharaohs had specially aligned pyramids, obelisks, and solar temples built in his honor.
During the Middle Kingdom, the new deity, Amun-Ra was formed. Amun was one of the gods who formed the Ogdoad (the assembly of eight gods who represented eight elements of creation).
It appears almost certain, that the Great Ennead – the nine deities of Atum, Geb, Isis, Nut, Osiris, Nephthys, Seth, Shu, and Tefnut – first appeared during the decline of Ra’s cult in the sixth dynasty, and that after introduction of the new pesedjet the cult of Ra soon saw a great resurgence until the worship of Horus gained prominence.
As the king and leader of Egypt, the pharaoh was seen as the human manifestation of Horus, so the two gods became connected. This new deity fusion was then referred to as “Ra-Horakhty” meaning Ra is Horus of the Horizon. Ra’s relationship with other gods did not stop there. As the powerful creator of mankind and the sun god, he also became associated with Atum to make “Atum-Ra.”
Afterward worship focused on the syncretistic solar deity Ra-harakhty (Ra, who is Horus of the Two Horizons). During the Amarna Period of the eighteenth dynasty, Akhenaten introduced worship of another solar deity Aten. The deified solar disc represented his preferred regional deity as he attempted to lessen the influence of the temple of Atum. He built the Wetjes Aten (Elevating the Sun-disca) temple in Annu. Blocks from this temple later were used to build walls to the medieval city of Cairo and are included in some of the city gates. The cult of the Mnevis bull, an embodiment of Ra, had its centre here and established a formal burial ground for the sacrificed bulls north of the city.
In the later myths Ra was seen to have created Sekhmet, the early lioness war goddess who becomes Hathor, the cow goddess after she has sufficiently punished mankind as an avenging Eye of Ra.
This changes the themes of much earlier myths into aspects of his and he is often said to be the father of both, and brother, to the god Osiris. Afterward nearly all forms of life supposedly were created only by Ra, who called each of them into existence by speaking their secret names and eventually humans were created from Ra’s tears and sweat, hence the Egyptians call themselves the “Cattle of Ra.”
Although not the contemporary view, E. A. Wallis Budge (1857-1934) claims that Ra was the one god of Egyptian monotheism, of which all other deities were aspects, manifestations, phases, or forms.
During the New Kingdom, the worship of Ra became more complicated and grand. The walls of tombs were dedicated to extremely detailed texts that told of Ra’s journey through the underworld. Ra was said to carry the prayers and blessings of the living with the souls of the dead on the sun boat.
The idea that Ra aged with the sun became more popular with the rise of The New Kingdom. Eventually, during the reign of Akhenaten (mid 1350s-1330s), the worship reached the level of “uncompromising monotheism”
Many acts of worship included hymns, prayers, and spells to help Ra and the sun boat overcome Apep. Though worship of Ra was widespread, his cult center was in Heliopolis in Lower Egypt. Oddly enough, this was the home of the Ennead that was believed to be headed by Atum, with whom he was merged. The Holiday of ‘The Receiving of Ra’ was celebrated on May 26 in the Gregorian calendar.
Though Ra lived on in various forms into the Greco-Roman period, his worship gradually deteriorated during the fist millennium. This decline was probably due to the weakening of the kingship under various foreign rulers. Though he continued to be a part of Egyptian theology, he was no longer a part of the peoples living faith. Devotion to Ra became more and more limited to priests of the temple.
The rise of Christianity in the Roman empire caused an end to worship of Ra by the citizens of Egypt, and as Ra’s the popularity suddenly died out, the study of Ra became purely for academic knowledge even among the Egyptian priests.
Sources:
Holder of the Oath Ring; The Silent One

- Also known as: Oller, Ull, Uller, Ullr, Vuldor
- Origin: Norse:
- Rune: Ihwaz
- Tree: Yew (Holler’s home is Ydalir, Yew Tree Valley)
- Favored people: Holler likes the ladies. Skiers love Holler and he seems to love them right back.
Holler is the Lord of Frost and the King of Winter. He is a particularly primordial Norse deity, a mysterious, shadowy spirit. It’s unclear exactly where he sits on the Aesir / Vanir spectrum. Holler may be the son of Sif, the Golden-Tressed One. His father, if any, is unknown, although some suggest that he is of Frost Giant descent.
Holler’s name may be related to “glory.” He seems to have been venerated throughout Scandinavia, the Germanic lands, and the British Isles. According to some myths, when Odin goes wandering, he leaves Holler in charge of Asgard.
Holler is a master archer and hunter and a brilliant skier. Holler skis through the heavens, leaving stars in his wake. He controls the Aurora Borealis. Holler is the lord of justice and dueling. Allegedly invoking his name before a duel brings good luck. When he’s not zipping over the snow on his skis, Holler travels in a ship made from bone.
Holler the Hunter has associations with death. His sacred tree, the yew, is a funerary tree, found in grave yards, not least because of its poisonous berries. Holler may have hunted with poisoned arrows. He may be married to Hulda, weather goddess of birth and death. Like her, he is now associated with the Wild Hunt, and a more negative connotation as the God of Death, Disease and Devastation. It is said that he drags the doomed to his darkest dungeon and delights in dealing out disaster and destruction.
Post-Christianity, many of his more benevolent functions seem to have been transferred to Saint Hubert.
Source: The Encyclopedia of Spirits
Hekate is an exceptionally powerful spirit. She holds dominion over life, death, regeneration, and magic. She rules wisdom, choices, expiation, victory, vengeance, and travel. Hekate guards the frontier between life and death. She is an intermediary between the spirit world and that of humans. She is the witness to all crimes, especially those against women and children.
Hekate (Hecate) is Queen of the Night, the Spirit World, and Witchcraft. Her epithets include:
- She Who Works Her Will
- The Most Lovely One
- Influence From Afar
- Three Headed Hound of the Moon
- The One Before The Gate
- Light Bringer
Although today most associated with Greek mythology, her name, meaning “influence from afar,” acknowledges her foreign origins.
Generally believed to have first emerged in what is now Turkey, she was not an obscure goddess. Hekate was at one time chief deity of Caria, now western Turkey, and was eventually widely worshiped throughout Europe, Western Asia, and Egypt. Records of formal worship date from eighth century BC to the fourth century AD, although as magic fell from grace she became an increasingly disreputable spirit. All Hekate’s myths clearly identify her as a witch and matron of magical arts.
Hekate is renowned for her expertise with plants and her knowledge of their magickal and healing powers. A famed magickal garden was attached to her temple in Colchis on the Black Sea, now in modern Georgia. Some scholars suggest that an ancient Greek women’s guild, under the divine matronage of Hekate, once had responsibility for gathering and storing visionary, hallucinatory and poisonous plants. The same work in Greek indicates “pharmacist,” “poisoner,” and “witch.”
Petitioning Hekate
Hekate is a goddess of life, death, regeneration and magick. She rules wisdom, choices, expiation, victory, vengeance, and travel. She is witness to every crime.
- She is invoked for justice, especially for sexual crimes against women and girls.
- Hekate is invoked when justice is not forthcoming from other channels.
- Hekate has the power to grant or deny any mortal’s wish.
- She may be invoked for protection for dogs and from dogs.
- Hekate is petitioned for fertility, especially for female children.
- She brings victory in battle.
- Hekate may be invoked for healing, especially if medical solutions have failed.
- She may be petitioned for swift, painless death.
- Hekate can banish ghosts – or produce a ghost infestation.
Hekate typically responds to petitions via visions and dreams. If lost at a crossroads, literal or metaphoric, invoke her name and then pay attention to signs from her. She can be a shadowy, oblique goddess: her response may be subtle. Look for her animals: snakes, dragons, cats, and especially dogs.
- Favored people
Midwives, witches, healers, herbalists, dog lovers and rescuers. She is the matron of women in general and protects those who ride horses.
A Living Altar
Hecate is most famous today as a Dark Moon Spirit and Queen of Witches. Those are but two aspects of this multifaceted deity. Hecate was once the chief deity of the Carian nation, now in Western Turkey. She is matron of the city of Istanbul. She has dominion over life and death and makes the journey in between, indicating her power as a healing deity. Hecate is matron of midwives and herbalists.
Her priestesses (the most famous was Medea) were trained herbalists. Those in need of healing or solace journeyed to the gardens attached to Hecate’s shrine in Colchis on the Black Sea, home of the Golden Fleece pilfered by the Argonauts.
Hecate’s assistance may also be accessed by building a living altar in her honor. Plant a garden outdoors or create a living altar inside with potted plants. Add some or all of the following:
- Dog roses,
- Garlic,
- Lavender,
- Mandrake,
- Queen of the Night,
- Roses,
- Thorn apple,
- Tuberoses.
Hecate’s trees include:
- Black poplar
- Date palm
- Pomegranate
- Willow
- Yew
Place votive images of Hecate, together with her favorite creatures – dogs, dragons, and snakes – in the garden. To petition Hecate directly or to receive spontaneous magical inspiration regarding your healing needs, sit in or beside your living altar in the dark.
To Summon Hekate
Hecate, Queen of Witches, maintains office hours only at night: formal petitions and invitations must be offered after dark. A particularly ancient spirit, the only source of illumination she favors is fire.
Summon Hecate at night by a three-way crossroads. Ideally, light your way with a mullein torch. Offer her garlic, lavender, and honey. If you have a dog, bring it with you. Keep an eye on the dog; it’s likely to perceive Hecate before you do.
Why would you wish to contact Hecate?
Because she can teach you to do anything with magic. Because she can grant you enhanced psychic powers, fertility, romance, protection, freedom from illness, and magical restitution for any crime committed against you.
Hekate has been with us for at least three thousand years.
She was a liminal goddess who was present at all the boundaries and transitional moments in life. She was also an ‘evil-averting’ protector and guide. Her triple form emphasized her power over the three realms, these being the heavens, sea, and earth. Her primal nature was seen in the many animal heads she was depicted with, each emphasising different qualities of her manifold character.
Some of her well known titles include:
- Chthonia – earthy one
- Dadouchos – torch bearer
- Enodia – of the ways
- Kleidouchos – key bearer
- Kourotrophos – child’s nurse
- Phosphorus – light bearer
- Propolos – companion
- Propylaia – before the gate
- Soteira – savior
- Triformis – three bodied
- Trioditis – of the three ways
To enhance your ability to summon Hecate, try this:
Dry dandelion roots, then slice and pierce them to create beads, forming a ritual necklace to wear when calling Hecate. Call – or think – Hecate’s name as you pierce, string, and knot each bead. For best results, string the necklace at night by firelight.
Another way to enhance your relationship with the Queen of the Night is to practice the Silence of the Night Meditation. It’s a very simple yet profoundly powerful meditation, especially when practiced for an extended period of time.
Manifestations
Hekate has been known to assume the shape of a black cat, a bear, a pig or a hen but most typically manifests as a mature woman or black dog. She has a particularly strong bond with dogs. Even when manifesting in human form, Hekate is usually accompanied by hounds. Somehow there will be a canine reference. When manifesting as a woman alone, Hekate often circles in the manner of a dog.
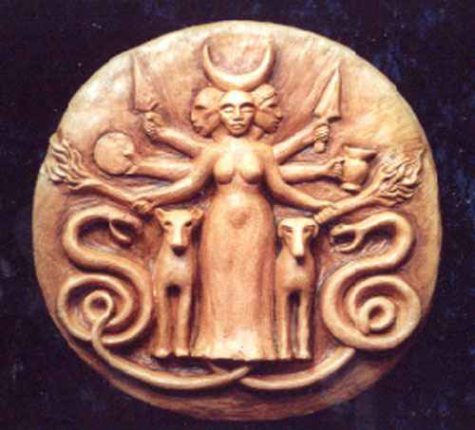
Artistic renderings of Hekate usually attempt to capture her spiritual essence. She may be depicted with three bodies, each facing a different direction. One hand holds the knife that is the midwife’s tool, another holds a torch to illuminate the darkness, the last bears a serpent representing medical and magical wisdom. Sometimes Hekate is depicted with a woman’s body but three animal heads – those of a dog, a horse, and a lion.
Hekate, Queen Witch, is a shape-shifter supreme. While her usual manifestations are as a black dog or mature woman, she may manifest as a haggard, decrepit crone or a sexy, elegant, seductive woman. She even has an occasional mermaid manifestation. She may wear snakes in her hair. Every now and then, she appears as a black cat, snake, or dragon.
Sacred to Hekate
Hekate’s sacred time is black night. All her festivities and ceremonies are held after dark, the only acceptable illumination is candles or torches. She only accepts offerings and petitions at night. Hekate is identified with the Dark Moon, the time of her optimum power.
The last day of each month is dedicated to Hekate. She also shared a festival with Diana on August 13th in Italy. Modern Wiccans, for whom Hekate is an important deity, celebrate November 16th as Hecate Night of the Crossroads.
- Animals: Black ewe lambs, Boar, Bull, Cats, Cock, Cow, Dogs, Dragons, Fish, Goats, Horses, Lions, Mice, Mullet (fish), Polecat, Rams, Serpents, Toads, Wolf
- Attributes: Key, Cauldron, Broom, Torch, Knife
- Bird: Stork
- Color: Black, also Red, White, Yellow
- Emblem: Star and crescent moon
- Food: Eggs, Honey, Amphiphon Cakes (a cheesecake with lighted candles stuck into it)
- Fruit: Pomegranate
- Minerals: Copper, Gold, Loadstone, Meteorite, Sapphire
- Mount: Dragons pull her chariot
- Number: Three
- Planets: Moon (especially the dark moon), and Sirius, the Dog Star
- Plants and herbs: Aconite, Anise, Belladonna, Garlic, Grain, Henna, Lavender, Mandrake, Onion, Poppy, Saffron,
- Symbols: Dagger, Keys, Horned Crescent, Pegasus, New Moon, Three-Way Crossroads, Trident, Twin Torches
- Trees: Apples, Black poplar, Date palm, Oak (leaves), Pomegranate, Willow, Yew
Her sacred place is the crossroads, specifically three-way crossroads. Among her name is Hecate Trivia. That doesn’t indicate that Hekate is trivial or that worshiping her was a trivial pursuit: Trivia literally means “three roads.” Hekate is Spirit of the Crossroads: her power emanates from their point of intersection. Hekate’s image was once placed in Greek towns wherever three roads met.
Hecate is the Goddess of the dark of the moon, the black nights when the moon is hidden. She was associated with deeds of darkness, the Goddess of the Crossways, which was held to be ghostly places of evil magic, an Awful Divinity,
“Hecate of hell
Mighty to shatter every stubborn thing.
Hark! Hark! Her hounds are baying through the town.
Where three roads meet, there she is standing.”
Rituals
Hekate’s ancient devotees held dinners in her honor, known as Hekate Suppers. Foods associated with her were prepared. The entree was usually fish, especially red mullet. Devotees feasted and celebrated. Offerings and leftovers were placed outside the door or at a crossroads for Hekate and her hounds.
- The last day of each lunar month is dedicated to Hekate.
- Friday the 13th – particularly if it falls in the month of August.
- November 16th is Hekate Night
- August 13th, in Italy, a festival is shared between Diana and Hekate
Even way back when, cynics scoffed that food placed outside was actually consumed by feral dogs and homeless people without realizing that this is Hekate’s intent: this is one way she accepts offerings. (The Church was still trying to eradicate this ritual as late as the eleventh century.)
Smaller, private offerings may be left at a crossroads, too:
- Place offerings on a plate or flat stone and leave them at a crossroads after dark.
- Make your invocation and then walk away without looking back.
- Do not return for the plate, or any part of the offering, but consider it part of your gift.
Offerings can include the following:
- Eggs
- Garlic and honey (especially lavender honey)
- Croissants and crescent shaped breads and pastries
- Candles
- Incense
- Images of dogs, especially black dogs
- Actions on behalf of dogs
Encountering or hearing a dog is an indication that your petition has been heard.
The Mythology
According to myth, Hekate once served as an Angelos, a messenger for the other deities. She stole Hera’s beauty salve to give to her rival Europa. Hera enraged, pursued Hekate, who fled first to the bed of a woman in childbirth, then to a funeral procession, and finally to Lake Acheron in Hades where she was cleansed by the Cabeiri. Hekate emerged more powerful than ever, a goddess of birth, death, and purification. She rules passages between realms of life and death and is thus invoked by necromancers.
Hekate is most prominent in Greek mythology for being the sole deity to voluntarily assist Demeter in her search for her abducted daughter, Persephone. Later, after Persephone eats Death’s six pomegranate seeds and is condemned to spend half the year in Hades, it is Hekate who accompanies her as Lady-in-Waiting. In some legends, she even becomes Hades’ co-wife. Ceberus, three-headed hound of Hades, may be Hekate in disguise.
Hekate becomes Persephone’s link to her mother and the land of the living. She guarantees that Death cannot break the bond between mother and daughter. Hekate is the Matron of Necromancy.
Hekate, daughter of the Titans Perses and Asteria, is older than the Olympian spirits. The eight-century BC Greek poet Hesiod writes that Hekate’s power dates “from the beginning.” Zeus was crazy about her: he eliminated all other pre-Hellenic deities (the Titans) but, having fallen madly in love with Hekate, he let her be.
Hekate is understood to be a triple goddess by herself, appearing as maiden, mother, and crone. She is also part of a lunar triplicity with Artemis and Selene, and also with Demeter and Persephone. Hekate dances in Dionysus’ retinue and is a close ally of Kybele.
Alongside her intense lunar identification, Hekate is also associated with the element of water: her first love affairs were with sea gods including Triton. Her great-grandfather was Pontus the Sea. Her maternal great-aunt was the sea monster Keto. Hekate is also related to the Gorgons and Sirens and may be the mother of Scylla, who was transformed into a sea monster by another relative, Circe. Prior to her transformation Scylla was a beautiful woman from head to waist, with canine hips terminating in a fish tale.
Hekate led a host of shape-shifting female spirits known as Empausas, whose usual manifestation was as a beautiful woman with one brass leg and one donkey’s leg; Hekate herself sometimes takes this form. The Empusas patrolled roads and apparently sometimes had fun terrorizing travelers. If one invoked Hekate, however, they left you alone.
Devotees feted the goddess by holding rituals known as Hecate’s Suppers at the end of each month at a crossroad. (The end of the month in lunar calendars corresponds to the Dark Moon, the new month begins with the first sighting of the new moon). The Church was still trying to eradicate Hecate’s Suppers in the eleventh century.
Post-Christianity, Hekate became among the most intensely demonized spirits, her very name synonymous with “witch”. Her symbols (toad, cauldron, broom) are inextricably linked with stereotypes of witchcraft. What were symbols of fertility became symbols of evil. Her sacred dogs were converted into the Hounds of Hell. This denigration served to camouflage Hekate’s origins as a deity of Healing and Protection.
An Interesting Historical Tidbit
Hekate was a goddess with an organized cult. In addition to Caria and Colshis, she had sanctuaries in Aigina and Lagina and a grove on the Aventine hill. She is the matron goddess and guardian of the city of Istanbul (previously called Byzantium and Constantinople).
Hekate is credited with saving that city from attack by King Phillip II of Macedonia in 304 BCE. His forces attempted to attack secretly during a dark moon but Hekate lit a crescent moon, creating enough light for the Byzantines to apprehend their danger and save themselves.
In gratitude, they began using her symbols (star and crescent moon) on their coins. The image still appears on the Turkish flag. The image predates Islam and was the official emblem of Byzantine Greeks.
Collected from various sources including Encyclopedia of Spirits
- Titles: The Mighty One, Great of Magic, Lady of Terror, Lady of Action, The One Before Whom Evil Flees, Mistress Dread, Lady of Flame, The Scarlet Woman
- Element: Fire
- Color: Red
- Consort: Ptah
- Son: Nefertem
- Origin: Upper Egypt
- Attribute: A two headed snake; Sekhmet holds one head in each hand. Also arrows
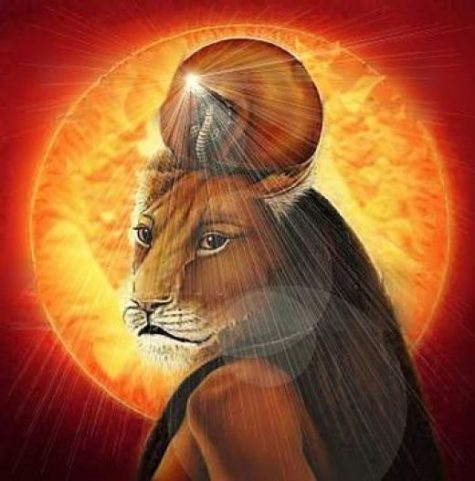
- Manifestation: Sekhmet manifests as a woman with a lion’s head or as a lioness.
- Feast Day: Feast of Sekhmet – Egyptian New Year’s Day – Jan 7
Sekmet, lioness goddess, epitomizes the blazing, scorching power of the sun. She is the goddess of war, justice, destruction, and healing. Her name may derive from a root word meaning “to be strong, powerful, mighty, or violent.” Sekhmet is among the fiery manifestations of the Eye of Ra.
She is a fierce guardian goddess of Upper Egypt. Her hot breath created the desert. Sekhmet was associated with plagues and pestilential diseases; illnesses that blew in on the desert winds. Sensational descriptions of Sekhmet tend to emphasize her destructive aspects, but she was also among Egypt’s most significant healing deities and remains an active healer today.
Sekhmet was represented by the searing heat of the mid-day sun (in this aspect she was sometimes called “Nesert“, the flame) and was a terrifying goddess. However, for her friends she could avert plague and cure disease. She was the patron of Physicians, and Healers and her priests became known as skilled doctors. As a result, the fearsome deity sometimes called the “lady of terror” was also known as “lady of life“. Sekhmet was mentioned a number of times in the spells of The Book of the Dead as both a creative and destructive force, but above all, she is the protector of Ma´at (balance or justice) named “The One Who Loves Ma´at and Who Detests Evil“.
Most spirits must be asked before they will openly intervene in someone’s life. (It’s possible that many perform acts of rescue anonymously). Sekhmet appears when invoked. She is also renowned for appearing in dreams and visions in order to perform successful healings even when no one summoned her, at least not consciously. Instead, Sekhmet recognized a need and personally took the initiative.
If Sekhmet heals you without first being asked, offerings are in order. Sometimes this is a one time favor but it may also be her way of extending matronage. If you wish to accept her offer, then create an altar or make some other gesture of acknowledgement.
Acceptable Offerings:
- Beer by itself or blended with pomegranate juice
- Arrows
- Silver medical tools
- Incense
Sekhmet heals all illnesses except those of the eyes. She is associated with blood ailments. She has dominion over the menstrual cycle and women’s reproductive systems. Sekhmet should not be bothered for trifles, but she is an intensely powerful and proactive healer. She is the matron goddess of reiki.